How to Write a Student SWOT Analysis
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on conducting a student SWOT analysis, a powerful tool to help students assess their academic strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This analysis is an essential step towards personal growth and academic success, enabling students to make informed decisions about their education and future careers. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the SWOT framework, providing a step-by-step guide and valuable insights to maximize its effectiveness. By the end of this article, students will have the knowledge and skills to conduct a thorough SWOT analysis, empowering them to take control of their academic journey.
Understanding the SWOT Framework
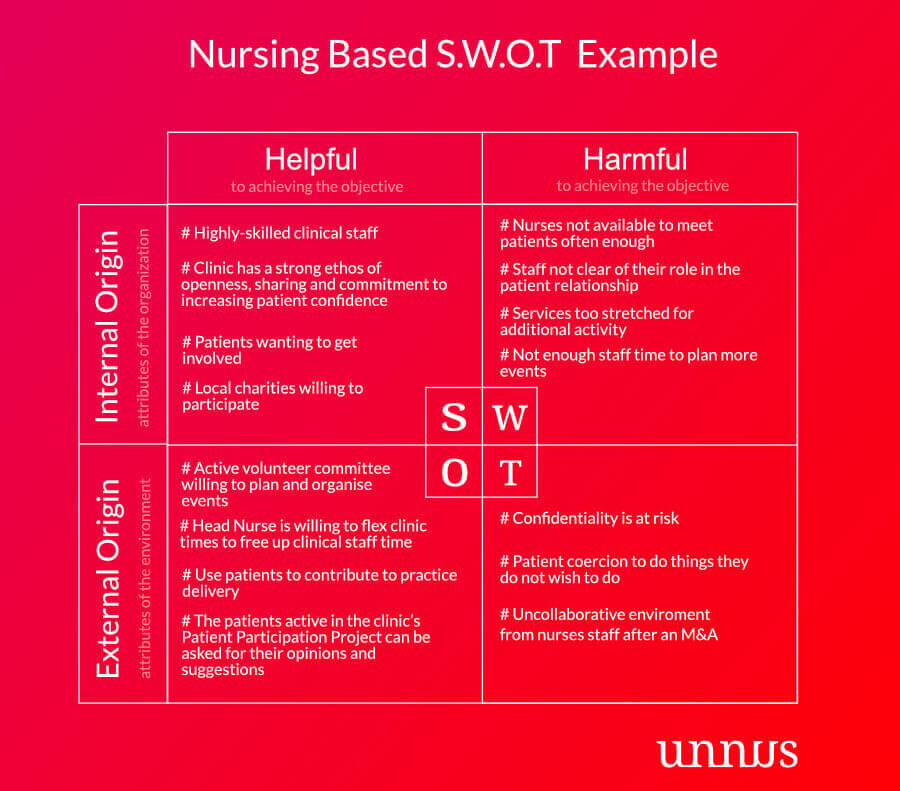
The SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used by individuals and organizations worldwide to evaluate their current situation and future potential. In the context of students, a SWOT analysis provides a structured approach to identify personal attributes, academic capabilities, and external factors that can impact their educational journey. This analysis serves as a roadmap, helping students set realistic goals, develop effective strategies, and make well-informed decisions about their academic pursuits.
Conducting a Student SWOT Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Define Your Academic Goals
Before embarking on your SWOT analysis, it is crucial to define your academic goals. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, you might aim to improve your GPA by a certain percentage within a defined timeframe, secure an internship in your desired field, or gain acceptance into a prestigious graduate program. Clearly defined goals provide a focal point for your SWOT analysis, ensuring that your evaluation is targeted and meaningful.
Step 2: Identify Your Strengths
Strengths are your personal and academic advantages, the factors that contribute to your success. These can include natural talents, skills you have developed, and positive traits that set you apart from others. For example, you might have exceptional communication skills, a knack for critical thinking, or a deep understanding of a particular subject. Identifying your strengths is crucial as it highlights your unique value and can guide you in leveraging these advantages to achieve your academic goals.
Step 3: Recognize Your Weaknesses
Weaknesses are areas where you lack proficiency or where you may struggle. These could be specific subjects or skills that you find challenging, personal traits that hinder your progress, or any other factors that could potentially hold you back. For instance, you might struggle with time management, have difficulty expressing yourself in writing, or lack confidence in public speaking. Recognizing your weaknesses is an important step, as it allows you to develop strategies to mitigate these challenges and turn them into opportunities for growth.
Step 4: Explore Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors that can enhance your academic journey. These could be emerging trends in your field of study, new courses or programs that align with your interests, or networking events that can connect you with industry professionals. For example, you might identify an upcoming conference where you can present your research, a scholarship program that can fund your studies, or a mentorship program that can guide your career path. Exploring opportunities helps you stay informed and proactive, ensuring that you can capitalize on these chances to further your academic goals.
Step 5: Assess Threats
Threats are external factors that could potentially hinder your academic progress. These could include competitive factors such as highly qualified peers, economic downturns that affect funding opportunities, or changes in educational policies that could impact your studies. For instance, you might face competition for internships or graduate programs, encounter financial challenges that impact your ability to pursue certain educational paths, or face unexpected changes in curriculum or assessment methods. Assessing threats is crucial as it allows you to develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate these risks, ensuring that you can navigate potential obstacles effectively.
Step 6: Integrate Your SWOT Analysis
Once you have identified your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it is time to integrate these elements into a comprehensive strategy. Start by matching your strengths with the identified opportunities. For instance, if you have strong research skills and an upcoming conference presents an opportunity to showcase your work, you can develop a plan to prepare and submit an abstract. Similarly, match your weaknesses with potential threats, and devise strategies to address or mitigate these challenges. For example, if you struggle with time management and face a heavy workload, you can develop a structured study plan to improve your efficiency.
Maximizing the Impact of Your SWOT Analysis
To ensure that your SWOT analysis is effective and actionable, consider the following best practices:
- Regularly update your SWOT analysis as your circumstances and goals evolve.
- Seek feedback from mentors, peers, or career counselors to gain fresh perspectives on your analysis.
- Break down complex goals into smaller, achievable tasks to make your SWOT analysis more actionable.
- Use your SWOT analysis as a living document, referring to it regularly to guide your decision-making and strategy development.
- Stay informed about industry trends and changes in your field of study to ensure your analysis remains relevant.
Conclusion
The SWOT analysis is a powerful tool for students to gain insight into their academic strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By conducting a thorough and regular SWOT analysis, students can make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and develop effective strategies to achieve academic success. This analysis empowers students to take control of their educational journey, ensuring that they make the most of their unique abilities and the opportunities available to them.
SWOT Analysis Example

Here is a sample SWOT analysis for a student aiming to pursue a career in data science:
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Strong mathematical foundation | Lack of experience with data visualization tools |
| Excellent problem-solving skills | Need to improve communication skills |
| Familiarity with programming languages | Limited knowledge of database management |

Opportunities:
- Growing demand for data scientists in various industries
- Online courses and boot camps to upskill quickly
- Opportunities for internships and collaborative projects
Threats:
- Highly competitive job market
- Rapidly evolving technology and skills requirements
- Potential for data privacy and security concerns
FAQ
How often should I update my SWOT analysis?
+It is recommended to update your SWOT analysis at least once a semester or whenever significant changes occur in your academic or personal life. Regular updates ensure that your analysis remains relevant and helps you stay proactive in managing your academic journey.
Can I conduct a SWOT analysis without any clear academic goals?
+While having defined academic goals can provide a clearer focus for your SWOT analysis, it is still beneficial to conduct an analysis even if you are unsure of your exact goals. The process of identifying your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can help you gain self-awareness and clarity, guiding you in setting realistic and achievable goals.
What if I can’t identify any strengths or weaknesses?
+If you struggle to identify your strengths and weaknesses, consider seeking feedback from mentors, teachers, or peers who can provide an objective perspective. Additionally, self-assessment tools and personality tests can help you gain insight into your unique qualities and areas for improvement.
How can I turn my weaknesses into opportunities for growth?
+Identifying your weaknesses is an important step towards personal growth. To turn these weaknesses into opportunities, develop a plan to address them. This could involve seeking additional support or resources, such as tutoring or online courses, to improve your skills. Additionally, consider how you can leverage your strengths to compensate for your weaknesses and create a well-rounded strategy.