Unleash The Power of Stacked Bar Charts
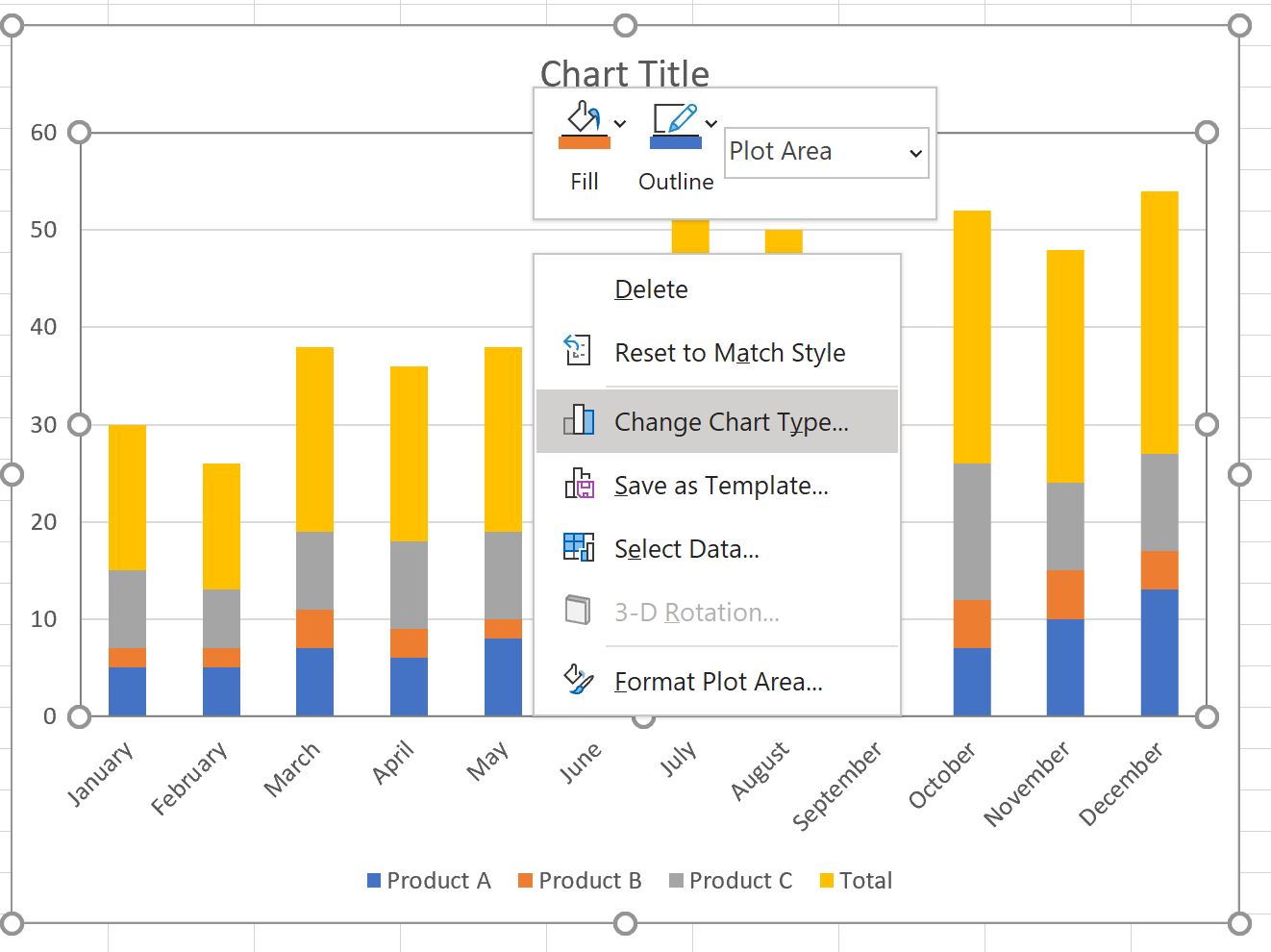
Stacked bar charts are an incredibly versatile and powerful tool for data visualization, offering a unique way to present and analyze complex datasets. By stacking multiple bars on top of each other, these charts provide a comprehensive view of the data, allowing for easy comparison and interpretation. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of stacked bar charts, exploring their benefits, best practices, and real-world applications. Get ready to unleash the full potential of this remarkable data visualization technique and discover why it is a favorite among data analysts and researchers.
Understanding Stacked Bar Charts
A stacked bar chart, also known as a stacked bar graph or stacked column chart, is a visual representation of data where each bar is divided into multiple segments, with each segment representing a different category or variable. This type of chart allows for the simultaneous display of multiple data series, providing a clear overview of the relationships and proportions between different components within a dataset.
Imagine you have a dataset that tracks the sales of different products over time. A stacked bar chart can showcase the sales of each product category, with the bars representing the total sales for a specific time period. By stacking the bars, you can easily compare the sales performance of each category and identify patterns or trends.
One of the key advantages of stacked bar charts is their ability to convey a wealth of information in a concise and visually appealing manner. They are particularly useful when dealing with datasets that have multiple dimensions or when you want to highlight the contribution of each component to the whole. Additionally, stacked bar charts can be customized with various color schemes and labeling options, making them highly adaptable to different data visualization needs.
Visualizing Proportions and Percentages
One of the primary strengths of stacked bar charts lies in their ability to showcase the proportional relationships between different categories or variables. By presenting data in a stacked format, it becomes evident how each segment contributes to the overall composition. This makes it easier to identify the dominant categories or to spot subtle differences between them.
Consider a scenario where you are analyzing the market share of different brands in a particular industry. A stacked bar chart can effectively display the market share of each brand, allowing you to quickly assess the relative strength of each player. Moreover, by incorporating percentages or labels on the chart, you can provide a more detailed understanding of the data, making it easier for viewers to grasp the significance of each segment.
Comparing Multiple Data Series
Stacked bar charts excel at facilitating comparisons between multiple data series. Whether you are tracking sales figures, market trends, or demographic data, a stacked bar chart can present a comprehensive overview of the relationships between different variables. By aligning the bars horizontally or vertically, you can easily identify patterns, similarities, or disparities between the data series.
For instance, imagine you are studying the voting patterns of different age groups in an election. A stacked bar chart can depict the voting preferences of each age group, with each bar representing a different candidate. By stacking the bars, you can quickly determine which age groups favor specific candidates and identify any significant deviations from the overall trend.
| Age Group | Candidate A | Candidate B | Candidate C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | 35% | 28% | 37% |
| 26-35 | 40% | 32% | 28% |
| 36-50 | 30% | 35% | 35% |
| 51+ | 25% | 45% | 30% |
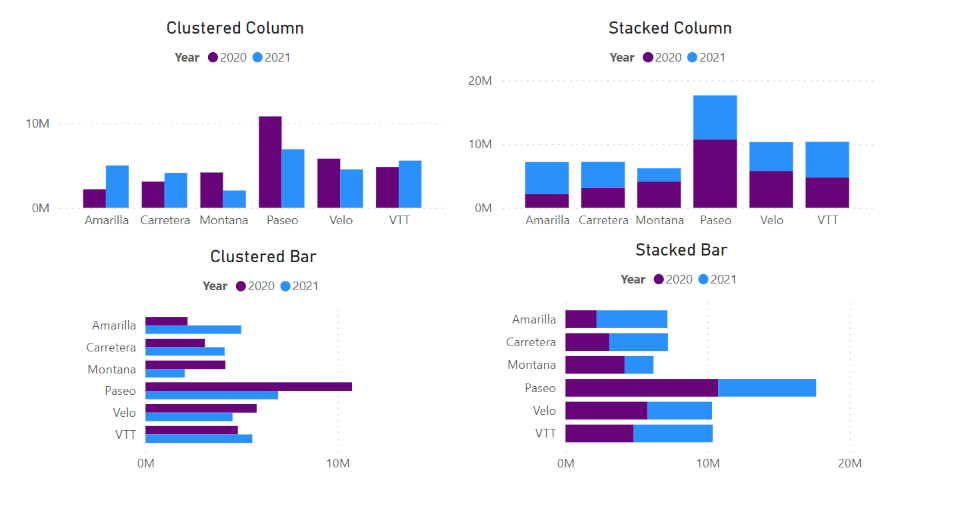
Best Practices for Creating Effective Stacked Bar Charts
To maximize the impact and effectiveness of stacked bar charts, it is essential to follow certain best practices. These guidelines ensure that your charts are not only visually appealing but also accurately convey the intended message. Here are some key considerations when creating stacked bar charts.
Choose the Right Data
Not all datasets are suitable for stacked bar charts. It is crucial to select data that has a clear hierarchical structure or where the relationships between categories are meaningful. Ensure that the data you choose aligns with the objectives of your analysis and that the stacked format will provide valuable insights.
For example, if you are analyzing the sales of different product lines, and each product line has distinct categories, a stacked bar chart would be an ideal choice. However, if your data consists of unrelated variables, a different chart type, such as a line chart or a scatter plot, might be more appropriate.
Labeling and Legends
Clear and concise labeling is essential for stacked bar charts. Ensure that the labels accurately describe the data and provide context to the viewers. Legends can be particularly useful when dealing with multiple data series or when the chart contains complex information. Legends should be positioned in a way that makes them easily accessible and understandable.
Consider using a legend that provides a brief description of each data series, especially if the categories are not immediately obvious. This helps viewers interpret the chart more effectively and allows them to focus on the key insights.
Color Selection
Color plays a vital role in data visualization, and stacked bar charts are no exception. Choose a color palette that is visually appealing and helps differentiate between the different segments of the chart. Avoid using colors that are too similar or that may cause confusion. Additionally, consider the color-blind accessibility of your audience and choose colors that are easily distinguishable for all viewers.
Some best practices for color selection include using a limited color palette to avoid overwhelming the viewer and ensuring that the colors have sufficient contrast. You can also consider using a diverging color scheme to highlight the extremes or a sequential color scheme to indicate a natural order or progression.
Order and Grouping
The order in which the categories are presented can impact the interpretation of the chart. Consider the natural order or hierarchy of the data and arrange the categories accordingly. This helps viewers understand the data more intuitively and makes it easier to identify patterns or trends.
For instance, if you are comparing the sales of different product categories over time, it might be more meaningful to order the categories based on their overall sales performance. This way, viewers can quickly grasp which categories are the top performers and which ones need attention.
Use of Percentages or Values
Deciding whether to display percentages or actual values on the chart depends on the nature of your data and the insights you want to convey. Percentages are often useful when you want to emphasize the proportional relationships between categories, especially when the absolute values are not as important.
On the other hand, displaying actual values can be beneficial when the magnitude of the data is crucial. For example, if you are tracking the growth of a company's revenue over time, showing the actual dollar amounts on the chart might provide a more accurate understanding of the financial performance.
Real-World Applications of Stacked Bar Charts
Stacked bar charts find applications in a wide range of industries and fields, offering valuable insights and aiding in decision-making processes. Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where stacked bar charts have proven to be an invaluable tool.
Market Analysis and Product Performance
In the business world, stacked bar charts are frequently used to analyze market trends and assess the performance of different products or services. By visualizing sales data or market share, companies can identify their best-performing products and make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and resource allocation.
For instance, a beverage company might use stacked bar charts to track the sales of different drink flavors over time. By analyzing the data, the company can determine which flavors are most popular and allocate resources accordingly, ensuring a balanced product portfolio.
Demographic and Social Research
Stacked bar charts are a powerful tool for researchers studying demographics, social trends, or public opinion. These charts can visually represent data collected from surveys, polls, or census records, allowing researchers to identify patterns, correlations, and shifts in various social indicators.
Consider a research study aiming to understand the voting behavior of different demographic groups. A stacked bar chart can effectively display the voting preferences of each group, helping researchers analyze the impact of factors such as age, gender, education, or income on voting decisions.
Environmental and Sustainability Studies
In the field of environmental science and sustainability, stacked bar charts can be instrumental in visualizing data related to energy consumption, waste management, or carbon emissions. By presenting data in a stacked format, researchers and policymakers can identify areas of improvement and develop targeted strategies for environmental conservation.
For example, a study on energy consumption in different sectors might use stacked bar charts to showcase the contribution of each sector to the overall energy usage. This visual representation can highlight the sectors that consume the most energy, prompting further investigation and the development of energy-efficient solutions.
Healthcare and Patient Data
Stacked bar charts find applications in healthcare settings, where they can assist in visualizing patient data, tracking disease prevalence, or analyzing the effectiveness of treatments. By presenting data in a stacked format, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into patient populations, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve patient care.
Imagine a hospital analyzing the distribution of different patient demographics, such as age, gender, and ethnicity. A stacked bar chart can effectively display this data, helping healthcare administrators understand the composition of their patient population and tailor their services accordingly.
Conclusion
Stacked bar charts are a versatile and powerful tool for data visualization, offering a unique perspective on complex datasets. By following best practices and leveraging their strengths, you can create compelling visualizations that communicate insights effectively. Whether you are analyzing sales data, studying social trends, or exploring environmental issues, stacked bar charts can provide valuable insights and support decision-making processes.
As you embark on your data visualization journey, remember to choose your data wisely, pay attention to labeling and legends, select appropriate color schemes, and consider the order and grouping of categories. With these best practices in mind, you'll be well-equipped to create stacked bar charts that are not only visually appealing but also convey meaningful and actionable information.
How do I choose the best color palette for my stacked bar chart?
+When selecting a color palette for your stacked bar chart, consider the number of categories you have and the level of contrast you need. A good rule of thumb is to use a limited color palette, typically no more than 5-7 colors, to avoid overwhelming the viewer. Choose colors that have sufficient contrast to ensure differentiation between categories. You can also explore colorblind-friendly palettes to ensure accessibility.
What is the difference between stacked and grouped bar charts?
+Stacked bar charts and grouped bar charts are both used to compare multiple data series, but they present the data in different ways. Stacked bar charts stack the bars on top of each other, allowing you to see the contribution of each category to the whole. Grouped bar charts, on the other hand, display the bars side by side, making it easier to compare the values of different categories directly.
Can I use stacked bar charts for time series data?
+Absolutely! Stacked bar charts are an excellent choice for visualizing time series data. By stacking the bars over time, you can easily track changes in the composition of your data and identify trends or patterns. Just ensure that your data has a clear temporal component and that the stacked format provides meaningful insights.
How do I ensure my stacked bar chart is accessible for colorblind viewers?
+To make your stacked bar chart accessible for colorblind viewers, you can follow a few simple guidelines. First, avoid using color combinations that are difficult to distinguish for those with color vision deficiencies. Instead, opt for colorblind-friendly palettes that provide sufficient contrast. Additionally, consider using patterns or textures alongside colors to enhance differentiation.