Mastering Milliseconds: Excel's Precision Tool
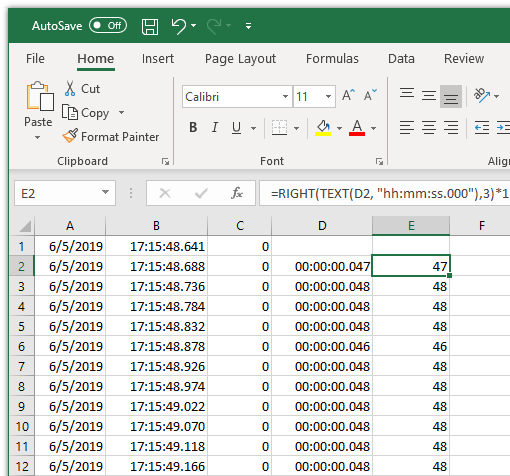
Welcome to the fascinating world of data precision in Microsoft Excel! Today, we delve into a powerful feature that often remains hidden beneath the surface—the precision tools within this widely-used spreadsheet software. Excel's precision capabilities offer an incredible level of detail and control, enabling users to work with data down to the millisecond and beyond. This precision is not just a technical curiosity; it's a vital asset for professionals in fields ranging from finance and science to data analysis and project management. As we explore Excel's precision features, we'll uncover their practical applications, benefits, and limitations, and learn how to harness this powerful functionality to gain a competitive edge in the world of data-driven decision-making.
The Significance of Millisecond Precision
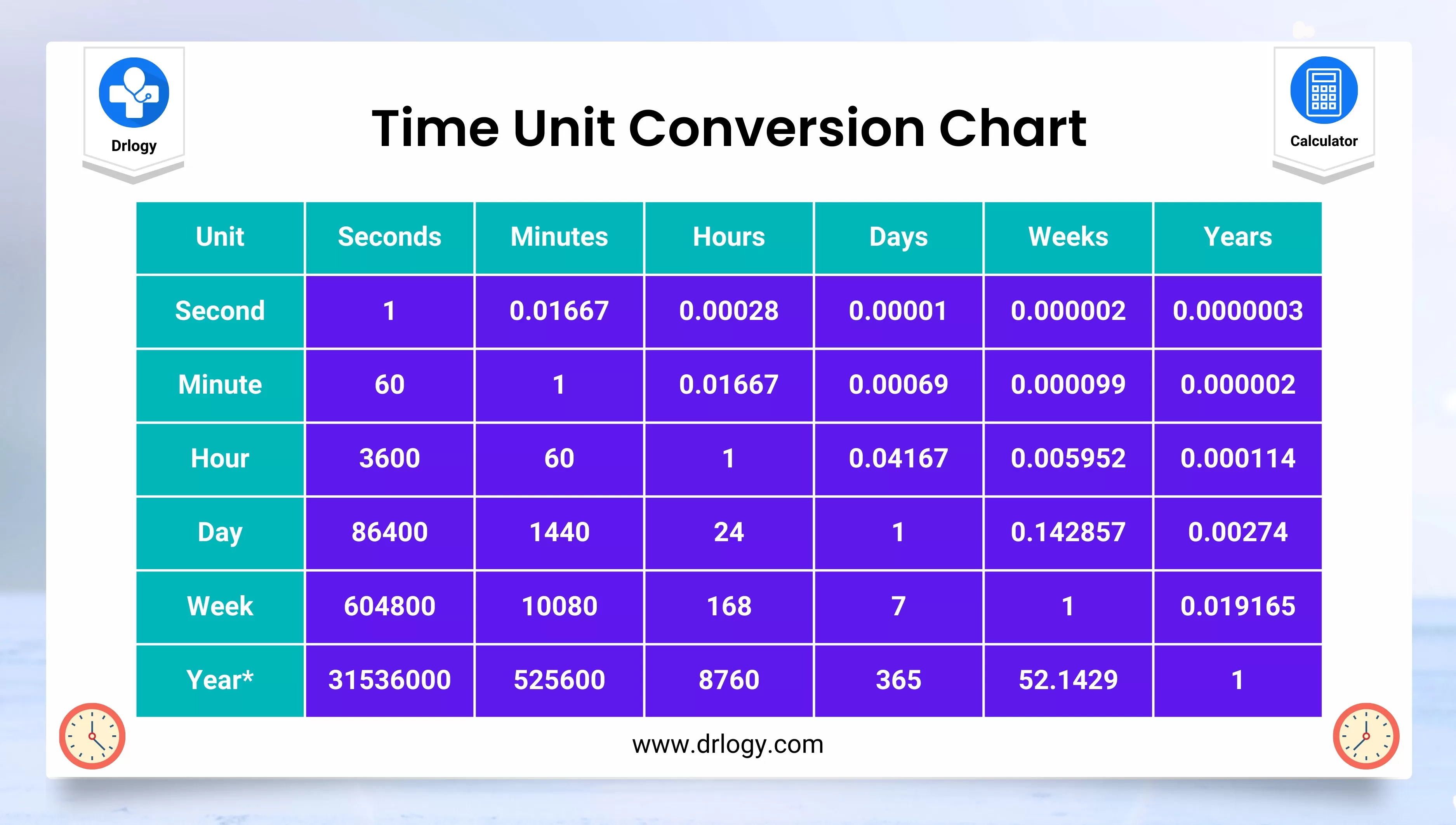
In the digital era, time is a critical factor in almost every industry. Whether it’s tracking financial transactions, monitoring scientific experiments, or managing project timelines, the ability to record and analyze data with millisecond accuracy can provide a significant competitive advantage. Excel’s precision tools allow users to work with time-sensitive data in a way that was previously only possible with specialized software. This precision can be a game-changer, especially when dealing with large datasets or real-time data streams.
Applications Across Industries
Excel’s millisecond precision finds applications in a wide range of sectors. For instance, in finance, it enables traders to track stock prices and execute trades with unparalleled speed and accuracy. In scientific research, this precision can be crucial for recording and analyzing experimental data, especially in fields like physics or environmental science where data collection often occurs in rapid bursts. For data analysts, it offers the ability to perform intricate time-series analyses, revealing trends and patterns that might otherwise be missed.
| Industry | Precision Application |
|---|---|
| Finance | High-frequency trading, transaction analysis |
| Science | Real-time data collection and analysis |
| Data Analysis | Time-series analysis, data visualization |
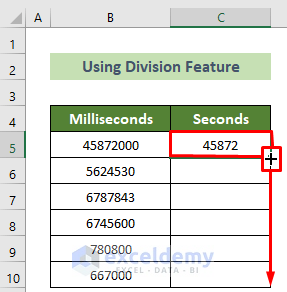
Excel’s Precision Tools: A Deep Dive
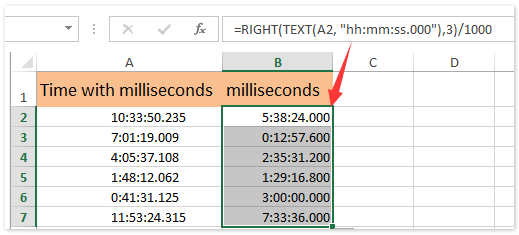
Excel provides a range of features and functions that enable users to work with time and date data with remarkable precision. These tools are not just about accuracy; they also offer a high degree of flexibility and customization, allowing users to adapt their data analysis methods to suit their specific needs.
Working with Time and Date Data
At its core, Excel stores time and date data as a single numerical value, with the integer portion representing the date and the decimal portion representing the time of day. This format allows for seamless mathematical operations and precise comparisons. Users can input time and date data in various formats, from standard date-time stamps to custom formats like “dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss”. Excel’s FORMAT function further enhances this flexibility, allowing users to display time and date data in a wide range of styles, from 24-hour clocks to custom date formats.
Excel also provides a range of functions for manipulating time and date data. For instance, the TIME function allows users to input time data as separate hours, minutes, and seconds, while the NOW function returns the current date and time. These functions, combined with Excel's calculation capabilities, offer a powerful toolkit for working with time-sensitive data.
Calculating Time Durations
One of the most powerful applications of Excel’s precision tools is the ability to calculate time durations with millisecond accuracy. This is particularly useful for tasks like calculating the duration of a project, the time between events, or the elapsed time between two timestamps. Excel’s DATEDIF function is a versatile tool for calculating time differences, offering options to calculate durations in years, months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds. For even more precise calculations, users can utilize the MOD function to extract the fractional part of a time value, allowing for calculations down to the millisecond.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| DATEDIF | Calculates the difference between two dates, offering a range of output options |
| MOD | Returns the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor, useful for extracting fractional parts of time values |
Visualizing Time Data
Excel’s precision tools are not just for calculations; they also enable users to visualize time-series data with incredible detail. Excel offers a range of chart types suitable for time-based data, including line charts, area charts, and bar charts. These charts can be further customized to display time data in a way that highlights the desired trends and patterns. For instance, users can use Excel’s Format Axis feature to adjust the time scale, allowing for visualizations that range from yearly to hourly intervals.
Excel's precision tools also enable the creation of sophisticated dashboards and reports that track and visualize time-based data. These dashboards can be updated in real-time, offering a powerful tool for monitoring and analyzing time-sensitive metrics.
Limitations and Workarounds
While Excel’s precision tools offer incredible capabilities, they are not without limitations. One key limitation is the potential for rounding errors when working with very large datasets or extremely precise time values. Excel’s internal precision is limited to 15 digits, which can lead to small discrepancies when working with very precise data.
Another challenge is the complexity of some precision calculations. While Excel provides a range of functions for working with time and date data, more complex calculations may require a deeper understanding of Excel's formula language and the use of custom functions. This can be a steep learning curve for some users.
Strategies for Overcoming Limitations
To overcome these limitations, users can employ several strategies. For rounding errors, it’s often helpful to work with the most precise data possible, ensuring that calculations are performed with the highest level of accuracy. This may involve working with original data sources or utilizing Excel’s Precision as displayed option, which ensures that data is stored and displayed with the level of precision the user chooses.
For complex calculations, users can leverage Excel's powerful formula language and the vast array of functions it offers. For even more advanced calculations, users can create custom functions using Excel's VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) or utilize third-party add-ins that offer additional precision tools.
Future Trends in Excel Precision
As technology advances, the demand for even greater precision in data analysis is likely to grow. Microsoft, recognizing this need, has been continually enhancing Excel’s precision capabilities. Recent updates have introduced new functions and improved existing ones, offering users even more flexibility and accuracy when working with time-sensitive data.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see further advancements in Excel's precision tools. This may include the introduction of new functions specifically designed for time-series analysis, improved handling of large datasets, and enhanced visualization tools that offer even more detailed insights into time-based data.
Conclusion
Excel’s precision tools offer a powerful set of capabilities for working with time-sensitive data. From simple calculations to complex visualizations, these tools enable users to gain deep insights from their data. While there are limitations to be aware of, with the right strategies and tools, users can overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of Excel’s precision capabilities. As data becomes an increasingly valuable asset in today’s world, the ability to work with data down to the millisecond can provide a significant competitive advantage.
How accurate is Excel’s time and date data storage?
+Excel stores time and date data as a single numerical value, which allows for accurate mathematical operations and comparisons. The accuracy of this storage depends on the precision of the data input and the specific calculations performed.
What is the maximum precision Excel can handle for time values?
+Excel’s internal precision is limited to 15 digits, which is generally sufficient for most practical applications. However, for extremely precise calculations, users may need to employ additional strategies or utilize specialized software.
Are there any alternatives to Excel for working with millisecond-precise data?
+Yes, there are specialized software tools designed specifically for working with time-series data, such as MATLAB or specialized database software. These tools offer advanced capabilities for handling large volumes of precise time-based data.