Say Goodbye to Scientific Notation in Excel
For anyone who has ever worked with scientific data in Excel, the concept of scientific notation is all too familiar. While this format can be useful for representing extremely large or small numbers, it often presents a challenge when it comes to data analysis and presentation. Scientific notation, with its use of exponential values, can make it difficult to interpret data at a glance and may even lead to errors if not handled properly. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to bid farewell to scientific notation in Excel, offering practical solutions and expert insights to ensure your data is presented in a clear and meaningful manner.
Understanding Scientific Notation in Excel
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in standard decimal format. In Excel, numbers are displayed in scientific notation when they exceed a certain magnitude, typically 1E+307 or -1E-307. This notation is represented as a number multiplied by 10 raised to an integer power, such as 1.23456789E+09, which is equivalent to 1.23456789 x 10^9.
While scientific notation is useful for handling extreme values, it can become a hindrance when it comes to data analysis and communication. For instance, when dealing with financial data, scientific notation can obscure important decimal places, making it difficult to identify trends or outliers. Similarly, in scientific research, precise values are crucial, and scientific notation may not provide the level of detail required.
The Impact of Scientific Notation on Data Interpretation
The use of scientific notation in Excel can significantly impact how data is perceived and analyzed. For one, it can make data comparison challenging. When numbers are displayed in scientific notation, it becomes harder to quickly assess which values are larger or smaller, as the exponential part of the notation can distract from the actual magnitude of the number.
Furthermore, scientific notation can introduce errors into calculations. Excel's built-in functions may not always interpret scientific notation correctly, leading to incorrect results. This is particularly true when working with complex formulas or when combining data from different sources with varying number formats.
Strategies to Avoid Scientific Notation in Excel
Adjusting Cell Formatting
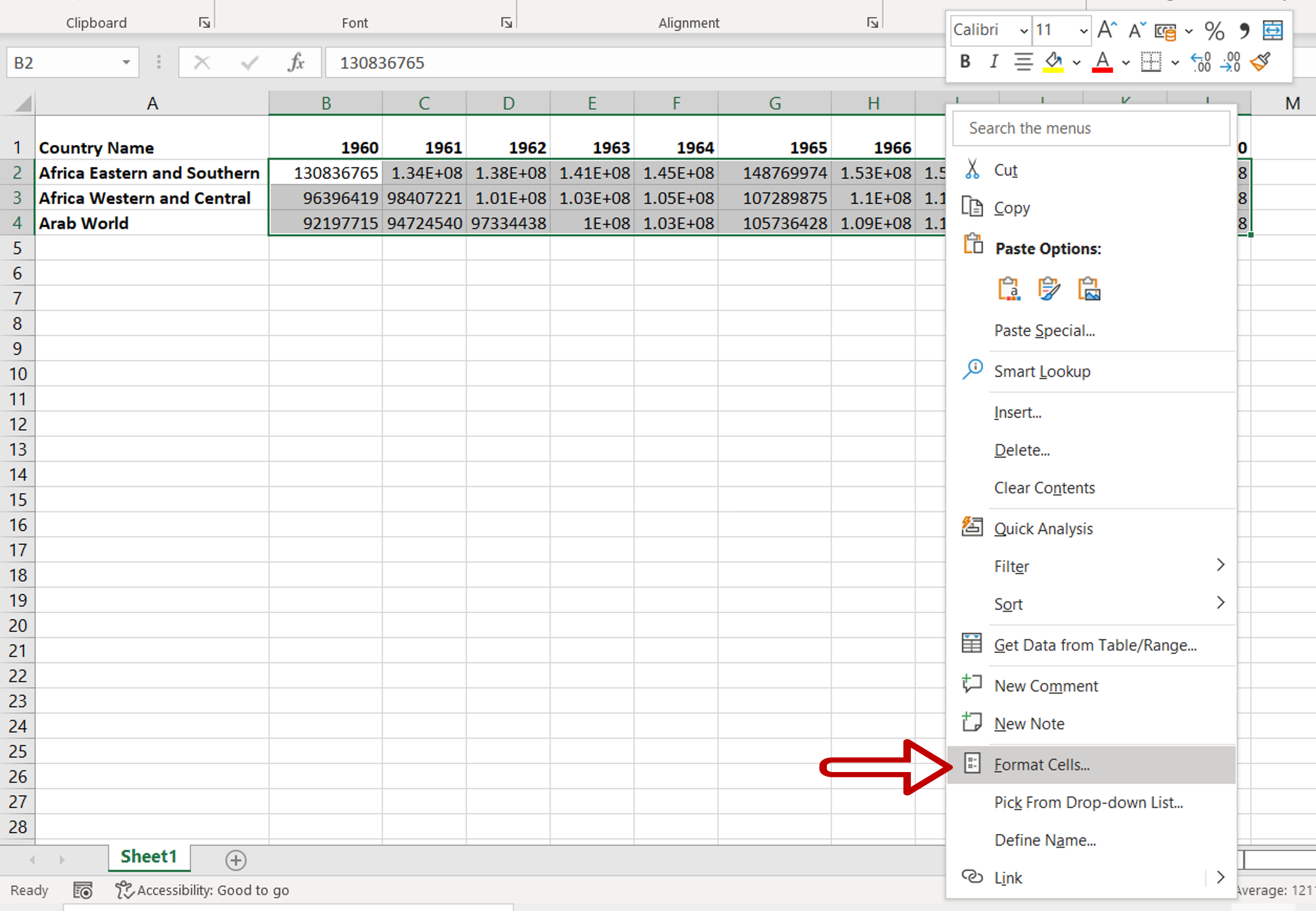
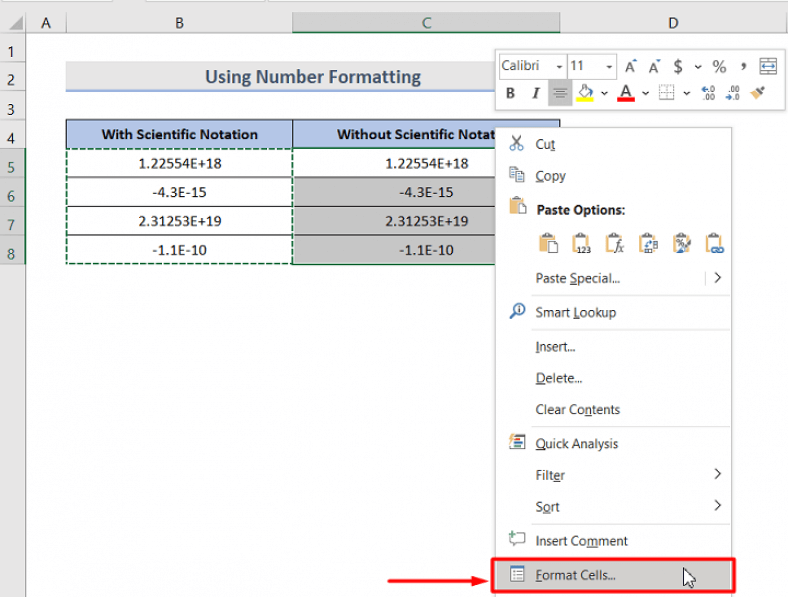
One of the simplest ways to prevent Excel from displaying numbers in scientific notation is by adjusting the cell formatting. To do this, select the cells you wish to format, right-click, and choose “Format Cells”. In the Format Cells dialog box, navigate to the “Number” tab. Here, you can choose from a variety of number formats, including “Number”, “Currency”, “Percentage”, and “Scientific”. By selecting the appropriate format and specifying the desired number of decimal places, you can ensure that your data is displayed as desired.
Using Custom Number Formats
Excel also allows you to create custom number formats to suit your specific needs. This is particularly useful when you want to display numbers with a certain level of precision or in a particular format. To create a custom number format, follow the same steps as above to access the “Format Cells” dialog box. In the “Type” field, you can enter your custom format using a combination of symbols and codes. For example, to display numbers with two decimal places and a comma separator for thousands, you can use the format ”#,##0.00”.
Applying Data Validation Rules
If you want to ensure that data entered into a particular cell or range adheres to a specific format, you can use Excel’s Data Validation feature. This tool allows you to set rules for the type of data that can be entered into a cell. To access Data Validation, select the cells you wish to validate, go to the “Data” tab, and click on “Data Validation”. In the Data Validation dialog box, you can choose from various validation criteria, including “Whole Number”, “Decimal”, “List”, and more. By setting the appropriate criteria, you can prevent users from entering data in scientific notation.
Advanced Techniques for Data Formatting
Utilizing Excel Functions for Number Formatting
Excel provides a range of functions that can be used to format numbers dynamically. These functions offer more flexibility than static formatting options and can be particularly useful when working with large datasets or when the desired format varies based on certain conditions. For example, the TEXT function allows you to convert a value to text in a specified format. The NUMBERVALUE function, on the other hand, converts a number stored as text to a numeric value. These functions can be used in combination with other Excel functions to create powerful data formatting solutions.
Conditional Formatting for Highlighting Specific Data
Conditional formatting is a powerful Excel feature that allows you to apply formatting based on certain conditions. This can be particularly useful when you want to highlight specific data points, such as numbers that are close to scientific notation limits. To apply conditional formatting, select the cells you wish to format, go to the “Home” tab, and click on “Conditional Formatting”. Here, you can choose from various built-in rules or create a custom rule to format your data based on specific criteria.
Macros for Automating Number Formatting
If you find yourself regularly dealing with data that needs to be formatted to avoid scientific notation, you may want to consider using Excel macros. Macros are a series of commands that automate tasks in Excel. By creating a macro to format numbers as needed, you can save time and ensure consistency across your worksheets. To create a macro, go to the “Developer” tab, click on “Record Macro”, perform the actions you want to automate (such as applying a specific number format), and then stop the recording. You can then assign the macro to a button or shortcut for easy access.
Best Practices for Presenting Data Without Scientific Notation
Consistency in Number Formatting
When presenting data, consistency in number formatting is key. Ensure that all numbers are displayed using the same format, whether it’s a percentage, currency, or a specific number of decimal places. This consistency makes it easier for your audience to interpret the data and compare values.
Using Charts and Graphs for Visual Representation
Sometimes, the best way to present data is through visual representations such as charts and graphs. Excel offers a wide range of chart types, from bar charts and line graphs to pie charts and scatter plots. By selecting the appropriate chart type and applying the right formatting, you can create compelling visual aids that communicate your data effectively. When creating charts, consider the type of data you’re presenting and the message you want to convey.
Providing Clear Labels and Legends
Clear labels and legends are essential for ensuring that your audience understands the data being presented. When creating charts or graphs, make sure to provide descriptive labels for axes, data series, and any other elements. This helps your audience quickly grasp the key takeaways from your data visualization.
Future Implications and Tips for Data Management
As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, effective data management becomes increasingly important. By avoiding scientific notation and adopting clear, consistent number formatting practices, you can ensure that your data is easily interpretable and accessible. This is especially crucial when sharing data with colleagues or clients who may not be as familiar with Excel’s features.
Furthermore, consider implementing a standardized data management system that encompasses not just number formatting but also data entry, validation, and storage. This can help reduce errors, improve data quality, and streamline your data analysis processes.
Conclusion
Saying goodbye to scientific notation in Excel is not just about aesthetics; it’s about ensuring that your data is presented in a way that is clear, accurate, and accessible. By employing the strategies outlined in this article, you can take control of your data formatting and enhance the quality of your data analysis and presentation. Remember, effective data communication is a key skill in today’s data-driven world, and mastering Excel’s number formatting tools is an essential step towards achieving this goal.
How can I prevent Excel from automatically switching to scientific notation when entering large numbers?
+To prevent Excel from automatically switching to scientific notation, you can adjust the cell formatting. Select the cells you wish to format, right-click, and choose “Format Cells.” In the Format Cells dialog box, navigate to the “Number” tab and choose a format such as “Number” or “Currency.” By specifying the desired number of decimal places, you can ensure that your data is displayed as desired without scientific notation.
What is the difference between scientific notation and standard number formatting in Excel?
+Scientific notation is a way of representing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in standard decimal format. It uses a number multiplied by 10 raised to an integer power, such as 1.23456789E+09. Standard number formatting, on the other hand, presents numbers as they are, with a specified number of decimal places, such as 1,234,567.89.
Can I use Excel functions to automatically format numbers to avoid scientific notation?
+Yes, Excel provides functions such as TEXT and NUMBERVALUE that can be used to format numbers dynamically. The TEXT function allows you to convert a value to text in a specified format, while the NUMBERVALUE function converts a number stored as text to a numeric value. By combining these functions with other Excel functions, you can create powerful data formatting solutions.