The Ultimate Guide to Class D Amplifiers
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Class D amplifiers, an essential component in the world of audio technology. In this expert-crafted article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of Class D amplifiers, exploring their history, working principles, benefits, and applications. By the end of this guide, you will have a solid understanding of this revolutionary amplifier technology and its impact on the audio industry.
The Evolution of Class D Amplifiers
The story of Class D amplifiers begins with the quest for more efficient and powerful audio amplification systems. Traditional amplifier classes, such as Class A, B, and AB, have served as the foundation for audio amplification for decades. However, these classes have their limitations, particularly in terms of power efficiency and thermal management.
In the late 20th century, audio engineers and researchers sought to address these limitations by exploring new amplification techniques. This led to the development of Class D amplifiers, a technology that revolutionized the way we amplify audio signals.
Class D amplifiers, also known as switch-mode amplifiers, were first introduced in the 1950s. However, it was in the 1980s and 1990s that significant advancements were made, paving the way for their widespread adoption. The key innovation behind Class D amplifiers lies in their ability to efficiently convert audio signals into digital pulses, resulting in exceptional power efficiency and a unique set of advantages.
A Historical Perspective
The concept of using digital pulses for audio amplification can be traced back to early digital signal processing (DSP) techniques. As DSP technology evolved, researchers began exploring its potential in audio amplification, leading to the birth of Class D amplifiers.
One of the pioneers in this field was Dr. Richard L. White, who published a groundbreaking paper in 1974 titled "A Switching Amplifier with 90% Efficiency." This paper laid the foundation for the development of Class D amplifiers, showcasing their potential for high-efficiency audio amplification.
Over the years, numerous engineers and companies contributed to the refinement and popularization of Class D technology. Notable names include Dr. Peter Fischer, who developed the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) technique, and companies like Tripath, ICEpower, and B&O Play, which played crucial roles in bringing Class D amplifiers to the mainstream market.
Understanding the Principles of Class D Amplifiers
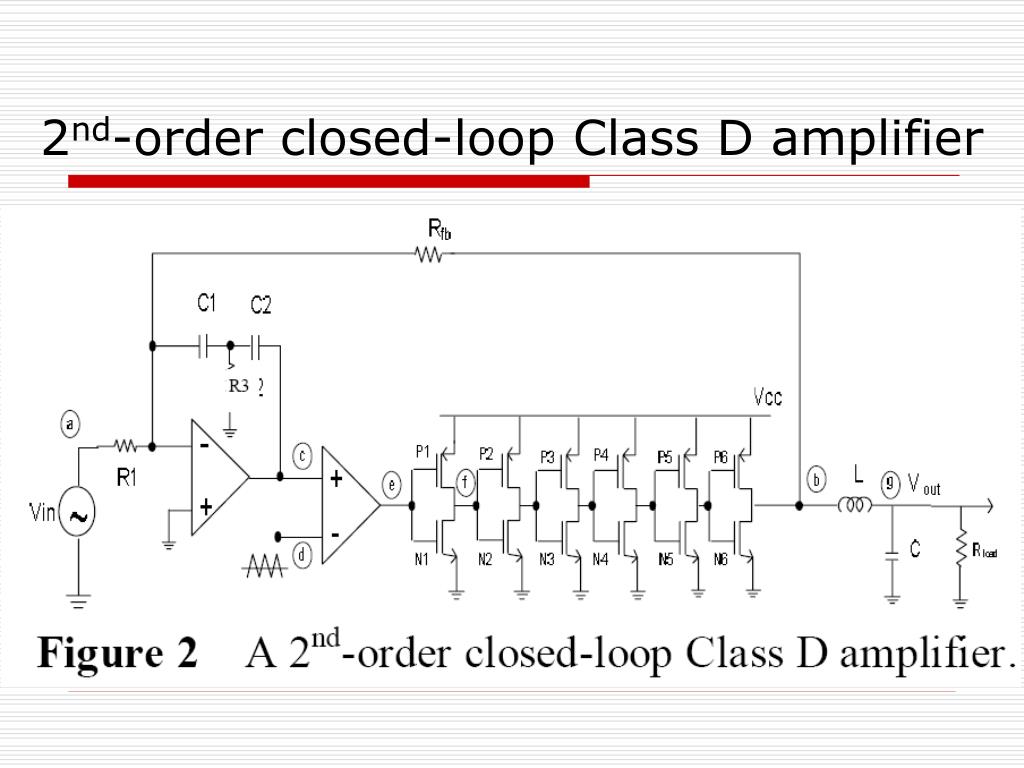
At its core, a Class D amplifier operates by converting an analog audio signal into a series of digital pulses. This process is known as pulse-width modulation or PWM. Unlike traditional amplifiers, which rely on linear amplification, Class D amplifiers employ a switching mechanism to control the flow of power.
Key Components and Functionality
A Class D amplifier consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in the amplification process.
- Input Stage: This stage receives the analog audio signal and prepares it for digital conversion. It typically includes an input buffer and a pre-amplifier circuit.
- PWM Modulator: The PWM modulator is the heart of the amplifier. It converts the analog signal into a series of digital pulses, typically using a comparator and a triangular waveform generator.
- Output Stage: The output stage of a Class D amplifier consists of high-speed power switches, usually MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors). These switches rapidly turn on and off, generating the digital pulses that represent the audio signal.
- Output Filter: To recreate the original analog audio signal, an output filter is employed. This filter removes unwanted high-frequency components, ensuring a clean and accurate audio output.
The Pulse-Width Modulation Process
The PWM process is a fundamental aspect of Class D amplifiers. It involves comparing the analog audio signal with a high-frequency triangular waveform. The comparator generates a digital pulse whose width varies depending on the amplitude of the audio signal.
For instance, when the audio signal is at its maximum positive amplitude, the pulse width is at its widest. As the audio signal decreases in amplitude, the pulse width narrows accordingly. This variation in pulse width directly corresponds to the amplitude of the audio signal, allowing for its accurate representation in digital form.
The resulting digital pulses are then amplified by the output stage, which rapidly switches the power supply on and off, creating a series of pulses that mimic the original audio signal. These pulses are then passed through the output filter, which reconstructs the analog audio signal for playback.
Advantages of Class D Amplifiers
Class D amplifiers offer a range of advantages that make them highly desirable in various audio applications.
Efficiency and Power Output
One of the most significant advantages of Class D amplifiers is their exceptional power efficiency. Unlike traditional amplifiers, which waste a considerable amount of power as heat, Class D amplifiers can achieve efficiencies of over 90%. This means less power is lost as heat, resulting in cooler operating temperatures and reduced energy consumption.
The high efficiency of Class D amplifiers allows them to deliver substantial power output without the need for large, heavy heat sinks. This makes them ideal for portable audio devices, where space and weight are critical factors.
Distortion and Noise
Class D amplifiers are known for their low distortion and noise levels. By converting the audio signal into digital pulses, they minimize the inherent non-linearities of traditional amplifiers. This results in a more accurate reproduction of the original audio signal, with lower levels of harmonic distortion.
Additionally, Class D amplifiers are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) due to their digital nature. This further contributes to their ability to deliver clean and distortion-free audio.
Thermal Management
The high efficiency of Class D amplifiers translates to better thermal management. Since less power is wasted as heat, these amplifiers can operate at cooler temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal damage and extending their lifespan.
This thermal advantage is particularly beneficial in high-power applications, where traditional amplifiers may require complex cooling systems to prevent overheating. Class D amplifiers can handle higher power outputs without the need for extensive thermal management solutions.
Size and Weight Considerations
Class D amplifiers are inherently smaller and lighter than their traditional counterparts. The elimination of bulky heat sinks and the use of compact switching components allow for more compact and portable audio systems.
This size advantage is especially crucial in applications such as car audio, home theater systems, and portable speakers, where space is often at a premium.
Applications of Class D Amplifiers
Class D amplifiers have found their way into a wide range of audio applications, thanks to their exceptional performance and versatility.
Car Audio Systems
In the automotive industry, Class D amplifiers are increasingly popular for their ability to deliver high-power audio performance in a compact and efficient package. They are commonly used in car audio systems to power subwoofers, speakers, and even entire audio setups.
The efficiency of Class D amplifiers ensures that car batteries are not excessively drained, while their compact size allows for more flexible installation options.
Home Theater Systems
Home theater enthusiasts often opt for Class D amplifiers to power their surround sound systems. The low distortion and high power output of Class D amplifiers enhance the audio experience, providing immersive and lifelike sound reproduction.
Additionally, the size and weight advantages of Class D amplifiers make them ideal for installing in home theater cabinets or entertainment centers, where space is limited.
Portable Speakers and Headphones
The portability and efficiency of Class D amplifiers make them a perfect fit for portable audio devices. From Bluetooth speakers to high-end headphones, Class D technology ensures that users can enjoy powerful audio performance without the bulk and weight of traditional amplifiers.
In the case of headphones, Class D amplifiers can deliver high-quality audio with minimal power consumption, extending battery life and providing an exceptional listening experience.
Professional Audio Equipment
Class D amplifiers have also found their place in professional audio equipment, such as PA systems and stage monitors. Their high power output, low distortion, and efficient thermal management make them ideal for demanding live performance environments.
Furthermore, the ability to stack multiple Class D amplifiers in parallel allows for scalable audio solutions, making them versatile for a range of professional audio applications.
Performance Analysis and Comparisons

To truly understand the capabilities of Class D amplifiers, it is essential to compare their performance with that of traditional amplifier classes.
Efficiency Comparison
| Amplifier Class | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| Class A | 15-25 |
| Class B | 50-70 |
| Class AB | 20-60 |
| Class D | 85-95 |
As shown in the table above, Class D amplifiers outperform traditional amplifier classes in terms of efficiency. This efficiency advantage translates to reduced power consumption, lower operating temperatures, and longer battery life in portable devices.
Distortion and Noise Analysis
Class D amplifiers are renowned for their low distortion and noise levels. While traditional amplifiers can suffer from various forms of distortion, Class D amplifiers minimize these issues through their digital switching mechanism.
The following table provides a comparative analysis of distortion levels for different amplifier classes:
| Amplifier Class | Distortion Level (%) |
|---|---|
| Class A | 0.1-1.0 |
| Class B | 0.1-1.0 |
| Class AB | 0.05-0.5 |
| Class D | 0.01-0.1 |
The low distortion levels of Class D amplifiers ensure a more accurate and faithful reproduction of the original audio signal, resulting in superior sound quality.
Future Implications and Innovations
The future of Class D amplifiers looks promising, with ongoing advancements and innovations shaping the audio industry.
Digital Signal Processing Integration
The integration of digital signal processing (DSP) capabilities with Class D amplifiers is a significant trend. DSP allows for advanced audio processing, such as equalization, crossover filtering, and dynamic range compression, directly within the amplifier.
This integration streamlines the audio system, reducing the need for separate DSP units and simplifying the overall setup. It also enables real-time audio adjustments, enhancing the user experience and system performance.
Wireless Audio Applications
The rise of wireless audio technologies, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, has created new opportunities for Class D amplifiers. These amplifiers can be integrated into wireless audio systems, providing efficient and powerful audio amplification for streaming services, smart home audio, and portable speakers.
The combination of Class D technology and wireless connectivity offers users the freedom to enjoy high-quality audio without the constraints of wired connections.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
With the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, Class D amplifiers are well-positioned to contribute to these goals. Their high efficiency reduces energy consumption, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Furthermore, the reduced power requirements of Class D amplifiers can lead to smaller and more efficient power supply designs, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Class A, Class B, and Class D amplifiers?
+
Class A amplifiers are known for their high-quality sound but are less efficient, as they consume more power. Class B amplifiers, on the other hand, are more efficient but can suffer from distortion at low signal levels. Class D amplifiers, or switch-mode amplifiers, are highly efficient and produce low distortion, making them ideal for modern audio applications.
Are Class D amplifiers suitable for high-end audio systems?
+
Absolutely! Class D amplifiers have advanced significantly in terms of sound quality and fidelity. They are now commonly used in high-end audio systems, offering excellent performance and efficiency. Many audiophiles and professionals prefer Class D amplifiers for their low distortion and accurate sound reproduction.
Can Class D amplifiers be used in home theater setups?
+
Yes, Class D amplifiers are an excellent choice for home theater systems. Their high power output, low distortion, and efficient thermal management make them ideal for delivering immersive surround sound experiences. Additionally, their compact size and weight make them easy to integrate into home theater cabinets.
Are there any drawbacks to using Class D amplifiers?
+
While Class D amplifiers offer numerous advantages, there are a few considerations. Some audiophiles argue that Class D amplifiers may have a slightly different sound signature compared to traditional amplifiers, which can be a matter of personal preference. Additionally, the high-frequency switching noise generated by Class D amplifiers can be a concern, although proper filtering techniques address this issue effectively.