Understanding Metered Networks: Unveiled
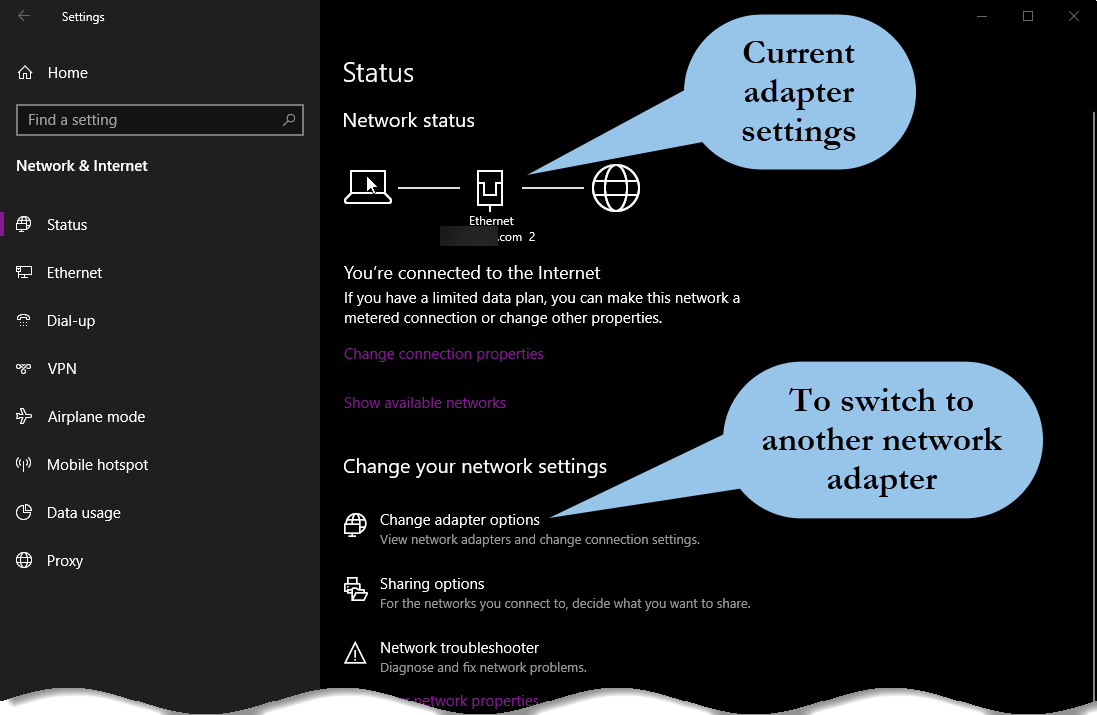
In today's digital age, internet connectivity has become an indispensable part of our lives, enabling seamless communication, access to information, and a host of online services. One crucial aspect of managing this connectivity is understanding the concept of metered networks. A metered network refers to an internet connection where data usage is carefully tracked and, in some cases, limited or charged accordingly. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of metered networks, shedding light on their functionality, benefits, and potential implications.
What are Metered Networks and How Do They Work?

Metered networks are designed to monitor and control data usage on a network, particularly in scenarios where internet access is provided by service providers with limited bandwidth or data caps. These networks employ various techniques to measure and manage data transmission, ensuring efficient and fair utilization of resources.
The operation of metered networks can be broken down into several key steps:
- Data Measurement: The network continuously monitors data packets transmitted and received by devices connected to it. This includes tracking the volume and nature of data, such as web browsing, streaming, downloads, and uploads.
- Data Thresholds: Service providers establish data usage thresholds or limits. Once a device exceeds these thresholds, the network may trigger specific actions to manage data consumption.
- Throttling or Shaping: When data limits are reached, the network might throttle the connection, reducing the speed temporarily or for specific activities. This helps ensure that all users receive a consistent level of service.
- Notification and Alerts: Metered networks often provide users with notifications and alerts when they approach or exceed their data limits. This allows users to monitor their usage and make informed decisions about their online activities.
- Billing and Payment: In certain cases, metered networks are associated with pay-as-you-go models, where users are charged based on their data consumption. This can be particularly relevant for mobile data plans or specialized internet services.
Real-World Examples of Metered Networks
Metered networks are prevalent in various contexts, including:
- Mobile Data Plans: Many mobile network operators offer metered data plans, where users pay for a certain amount of data and receive notifications when they approach their limits. This helps manage network congestion and ensures fair usage.
- Public Wi-Fi Hotspots: Public Wi-Fi networks, such as those in cafes or airports, often have data limits to prevent excessive usage and maintain network performance for all users.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Some ISPs implement metered networks for specific services or plans, especially for businesses with high-traffic websites or data-intensive operations.
- Limited-Bandwidth Environments: In remote areas with limited internet infrastructure, metered networks can help allocate resources efficiently, ensuring connectivity for all users within the network's capacity.
Benefits and Implications of Metered Networks

Metered networks offer several advantages, but they also present certain challenges and considerations.
Advantages
- Network Efficiency: By tracking and managing data usage, metered networks help optimize network performance. This is especially crucial in scenarios with limited bandwidth, ensuring that all users receive stable and reliable connectivity.
- Fair Usage: Metered networks promote equitable distribution of resources, preventing a few heavy users from overwhelming the network and affecting the experience of others.
- Cost Control: In pay-as-you-go models, metered networks provide users with cost transparency and control over their data consumption, making it easier to manage budgets.
- Performance Management: Service providers can identify and address potential issues or bottlenecks by monitoring data usage, leading to improved network stability and performance.
Potential Challenges
- Data Caps and Throttling: While data caps can be beneficial for network management, they might frustrate users who require higher data allowances or encounter unexpected data usage limits.
- Network Congestion: In scenarios where metered networks are not effectively managed, congestion can still occur, leading to slow speeds and degraded performance.
- Billing Complexity: Pay-as-you-go models may introduce complexities in billing and payment processes, requiring users to carefully monitor their usage and ensure timely payments.
- User Experience: The introduction of data limits and potential throttling can impact user experience, especially for activities like streaming or online gaming that require uninterrupted, high-speed connections.
Performance Analysis and Real-World Scenarios
To illustrate the impact of metered networks, let’s examine a few real-world scenarios:
Mobile Data Plans
Mobile network operators often offer a range of data plans, from basic to unlimited. Metered networks play a crucial role in managing these plans by:
- Tracking data usage to ensure accurate billing.
- Notifying users when they approach their data limits, allowing them to adjust their usage or upgrade their plan.
- Throttling speeds for heavy users to maintain network stability and fairness.
Public Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi hotspots, such as those in airports or cafes, are commonly metered to:
- Prevent excessive usage by a single user, ensuring fair access for all.
- Manage bandwidth allocation to maintain stable connections for a large number of concurrent users.
- Provide time-based or data-based limits to encourage turnover and accommodate more users.
Business Internet Services
Metered networks are also employed by businesses to:
- Monitor and manage data usage, especially for high-traffic websites or data-intensive operations.
- Implement data caps to control costs and ensure efficient resource allocation.
- Identify and address potential performance issues or security threats based on data usage patterns.
Future Implications and Technological Advances
As technology continues to evolve, metered networks are likely to play an even more significant role in managing internet connectivity.
Here are some potential future implications and advancements:
- 5G and Beyond: With the rollout of 5G networks and future generations of mobile connectivity, metered networks will be crucial in managing the increased data demands and ensuring efficient allocation of resources.
- Edge Computing: The rise of edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the source, may lead to more sophisticated metered networks that can dynamically allocate resources based on real-time usage patterns.
- AI-Powered Network Management: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can enhance metered networks by predicting and managing data usage trends, optimizing network performance, and providing personalized data plans based on user behavior.
- Enhanced User Experience: Future metered networks could offer more granular control and customization, allowing users to prioritize specific applications or activities, ensuring optimal performance for their most critical needs.
Conclusion
Metered networks are an essential component of modern internet connectivity, offering both benefits and challenges. As we navigate an increasingly data-intensive world, understanding and effectively managing metered networks will be crucial for individuals, businesses, and service providers alike. By striking a balance between resource management and user experience, metered networks have the potential to shape a more efficient, equitable, and sustainable digital future.
What is the primary purpose of metered networks?
+Metered networks primarily aim to manage and optimize data usage on a network, especially in scenarios with limited bandwidth or data caps. They help ensure fair and efficient allocation of resources, maintain network performance, and provide transparency to users regarding their data consumption.
How do metered networks affect user experience?
+Metered networks can impact user experience by introducing data limits and potential throttling. While this may frustrate users who require high data allowances, it also ensures that network performance is maintained for all users. Advanced metered networks can offer more customizable options to enhance user experience.
What are the potential benefits of metered networks for businesses?
+For businesses, metered networks offer benefits such as cost control, efficient resource allocation, and improved network performance. They can help identify and address performance issues, optimize data usage for high-traffic websites, and provide insights into data-intensive operations.



