5 Essential Computer Measurement Units
In the world of computer science and technology, measurement units play a vital role in understanding and quantifying various aspects of hardware, software, and network performance. These units provide a standardized way to communicate and analyze the capabilities and characteristics of computer systems. Among the multitude of measurement units available, there are five essential units that every computer enthusiast and professional should be familiar with. These units are not only fundamental to the field but also play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance, efficient resource allocation, and effective troubleshooting.
The 5 Essential Computer Measurement Units

Understanding these fundamental units is key to navigating the complex world of computer systems and ensuring that your hardware, software, and networks are performing optimally. Let's delve into each of these units and explore their significance, real-world applications, and the insights they provide.
1. Bits and Bytes: The Building Blocks of Data
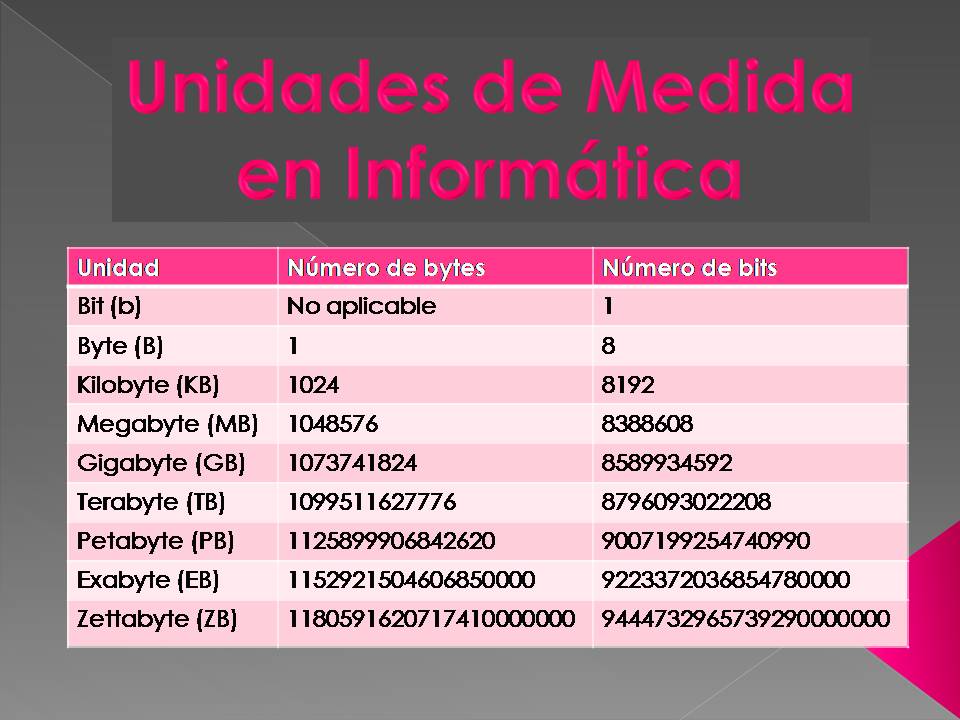
Bits and bytes are the fundamental units of digital information, serving as the building blocks of all computer data. A bit, short for binary digit, represents the smallest unit of data in a computer system and can have a value of either 0 or 1. On the other hand, a byte is composed of multiple bits, typically 8 bits, and is used to represent a single character or a small piece of information.
The use of bits and bytes allows for the efficient storage and transmission of data in computer systems. For instance, when you save a document or download a file, the data is stored or transferred in bytes. Similarly, when you measure the size of a storage device, such as a hard drive or a USB flash drive, the capacity is often expressed in bytes, such as megabytes (MB) or gigabytes (GB). Understanding bits and bytes is essential for managing data storage, transferring files, and ensuring that your computer system has sufficient capacity to handle your data needs.
| Unit | Definition | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Bit | A single binary digit, representing 0 or 1. | Data storage, data transmission, binary code. |
| Byte | A group of 8 bits, representing a single character or small data chunk. | File size, storage capacity, data processing. |

2. Hertz (Hz): Measuring Clock Speed and Frequency
Hertz, abbreviated as Hz, is the unit used to measure frequency, which is the number of cycles or events that occur per second. In the context of computers, Hz is often associated with clock speed, which refers to the frequency at which a computer's central processing unit (CPU) operates. The clock speed determines how quickly the CPU can execute instructions and process data.
A higher clock speed, measured in Hz, generally indicates a faster and more powerful CPU. For example, a CPU with a clock speed of 3.5 GHz (gigahertz) can process instructions and data at a rate of 3.5 billion cycles per second, making it a high-performance processor. Understanding clock speed is crucial for selecting the right CPU for your computer system, as it directly impacts the overall performance and responsiveness of your applications and tasks.
| Unit | Definition | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hertz (Hz) | Cycles per second, used to measure frequency and clock speed. | CPU clock speed, signal frequency, data transfer rates. |
3. Megahertz (MHz) and Gigahertz (GHz): Understanding Processor Performance
Megahertz (MHz) and gigahertz (GHz) are derived units of Hz and are commonly used to measure the clock speed of processors. While Hz represents cycles per second, MHz represents millions of cycles per second, and GHz represents billions of cycles per second.
For instance, a processor with a clock speed of 2.4 GHz can execute 2.4 billion cycles per second, indicating a high-performance capability. Understanding MHz and GHz is essential when comparing and selecting processors for your computer system. It allows you to gauge the processing power and performance potential of different CPU options, ensuring you choose the right processor for your specific needs, whether it's for gaming, content creation, or scientific computing.
| Unit | Definition | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Megahertz (MHz) | One million cycles per second, used to measure moderate clock speeds. | Older processors, lower-end devices. |
| Gigahertz (GHz) | One billion cycles per second, used to measure high-performance clock speeds. | Modern processors, high-performance computing. |
4. Terabytes (TB): Quantifying Storage Capacity
Terabytes (TB) are a unit of measurement used to quantify large amounts of digital storage capacity. A terabyte is equal to 1,024 gigabytes (GB) or 1,099,511,627,776 bytes. In the context of computer systems, terabytes are commonly used to measure the storage capacity of hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and other storage devices.
With the ever-increasing demand for data storage, terabytes have become a standard unit of measurement. For example, a modern desktop computer may come with a 1 TB hard drive, providing ample storage space for files, photos, videos, and software applications. Understanding terabytes is crucial when evaluating storage devices, as it helps you determine the capacity needed to store your digital content and ensure efficient data management.
| Unit | Definition | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Terabyte (TB) | Approximately 1 trillion bytes, used to measure large storage capacities. | Hard drives, solid-state drives, cloud storage. |
5. Pixels: The Building Blocks of Digital Images
Pixels, short for picture elements, are the smallest individual units that make up digital images. Each pixel represents a single dot or square of color on a screen or in an image file. The number of pixels in an image determines its resolution and quality. The more pixels an image has, the higher its resolution and the sharper the details.
Pixels play a crucial role in various aspects of computer systems, including display technology, digital photography, and graphic design. For instance, when you set the resolution of your computer monitor, you are essentially specifying the number of pixels that will be displayed on the screen. A higher pixel density, such as a 4K or Ultra HD display, offers a more detailed and immersive visual experience. Similarly, in digital photography, the number of pixels captured by a camera's sensor determines the image's resolution and print quality.
| Unit | Definition | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel | The smallest unit of a digital image, representing a dot of color. | Display resolution, digital photography, graphic design. |
The Impact of These Measurement Units
These five essential computer measurement units have a profound impact on the performance, functionality, and user experience of computer systems. From data storage and processing to display technology and digital imaging, these units shape the capabilities and limitations of modern computers.
By understanding and utilizing these measurement units effectively, computer enthusiasts and professionals can make informed decisions when selecting hardware, optimizing software, and troubleshooting performance issues. Whether it's choosing a processor with the right clock speed, allocating sufficient storage capacity, or ensuring high-resolution displays, these units provide the foundation for building and maintaining powerful and efficient computer systems.
As technology continues to advance, these measurement units will continue to evolve and adapt to meet the increasing demands of computer users. By staying updated on the latest advancements and trends, computer professionals can ensure that they are making the most of these fundamental units to deliver optimal performance and enhance the overall user experience.
What is the difference between bits and bytes in computer measurement units?
+
Bits and bytes are fundamental units of digital information. A bit represents a single binary digit, either 0 or 1, while a byte is composed of multiple bits, typically 8 bits, and represents a single character or a small piece of data.
How do Hertz (Hz) measure clock speed and frequency in computers?
+
Hertz (Hz) is the unit used to measure frequency, which is the number of cycles or events that occur per second. In computers, Hz is used to measure clock speed, which is the frequency at which a CPU operates. A higher clock speed, measured in Hz, indicates a faster and more powerful processor.
Why are Megahertz (MHz) and Gigahertz (GHz) important in processor performance measurement?
+
Megahertz (MHz) and Gigahertz (GHz) are derived units of Hz used to measure processor clock speed. MHz represents millions of cycles per second, while GHz represents billions of cycles per second. These units are important for comparing and selecting processors, as they indicate the processing power and performance potential of different CPU options.
How do Terabytes (TB) quantify storage capacity in computer systems?
+
Terabytes (TB) are a unit of measurement used to quantify large amounts of digital storage capacity. A terabyte is equal to 1,024 gigabytes (GB) or approximately 1 trillion bytes. TB is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of hard drives, solid-state drives, and other storage devices, helping users determine the capacity needed for their data.
What role do pixels play in digital imaging and display technology?
+
Pixels are the smallest individual units that make up digital images. Each pixel represents a single dot or square of color on a screen or in an image file. The number of pixels in an image determines its resolution and quality. Pixels play a crucial role in display technology, digital photography, and graphic design, impacting the visual experience and image quality.