Complete Guide: 5 Steps to Install Subfinder

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the importance of effective reconnaissance cannot be overstated. As an integral part of this process, Subfinder emerges as a powerful tool, offering a systematic approach to identifying subdomains. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the installation process, ensuring you harness the full potential of Subfinder to bolster your security practices.
Step 1: Acquiring Subfinder
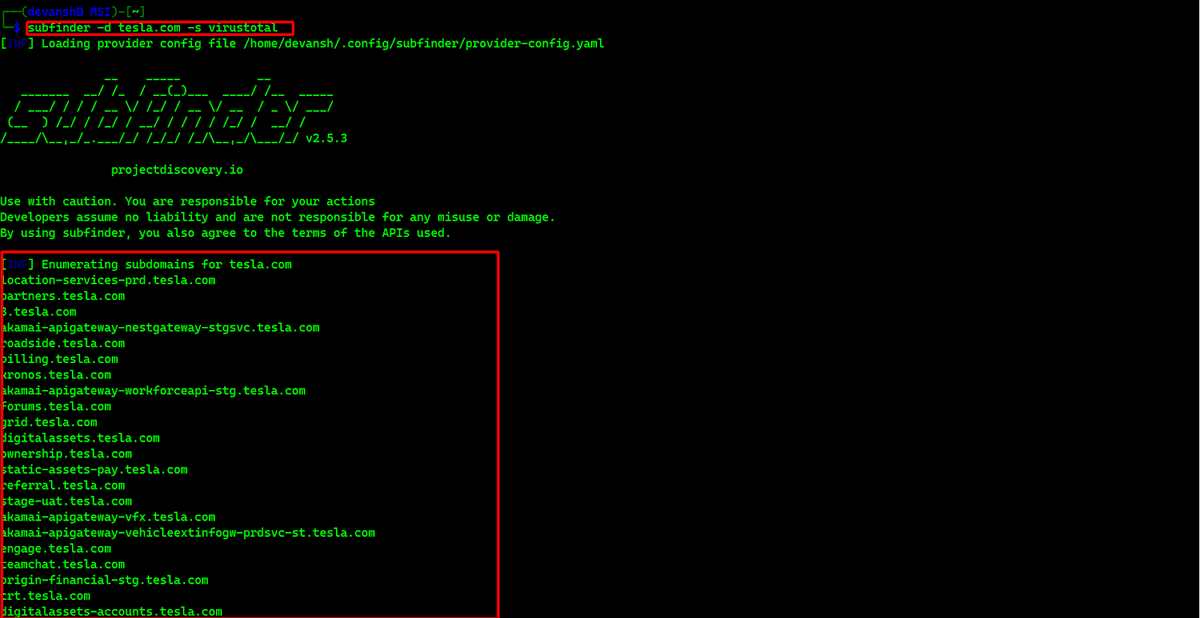
Subfinder is a command-line tool developed by ProjectDiscovery, renowned for its efficacy in subdomain discovery. It is an open-source tool, readily available for download from ProjectDiscovery’s GitHub repository. The repository provides detailed instructions for downloading and installing Subfinder, ensuring a straightforward process.
Step 2: Setting Up Your Environment
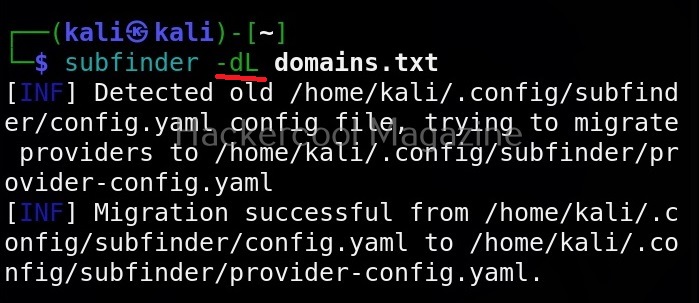
Before diving into the installation, ensure your system meets the necessary prerequisites. Subfinder is compatible with Linux, macOS, and Windows operating systems, and requires a stable internet connection for optimal performance. Additionally, having Python installed is crucial, as Subfinder is written in Python.
To verify Python's installation, open your terminal or command prompt and type:
python --version
If Python is installed, it will display the version number. If not, follow the installation instructions provided by the official Python website.
Step 3: Installing Subfinder
With the prerequisites in place, it’s time to install Subfinder. Navigate to the Subfinder GitHub repository and locate the Downloads section. Here, you will find the latest release of Subfinder, which you can download by clicking on the Assets link. Choose the appropriate file for your operating system.
Once downloaded, extract the contents of the archive. You should now have a folder named subfinder containing the Subfinder executable file and associated scripts.
For Linux and macOS users, ensure the executable file has the necessary permissions by running:
chmod +x subfinder
Now, move the subfinder folder to a directory in your PATH, such as /usr/local/bin or $HOME/bin, to ensure Subfinder can be accessed from anywhere on your system.
Windows users can simply copy the subfinder.exe file to a directory of their choice and add that directory to the system's PATH environment variable. This step ensures that Subfinder can be run from any location on the system.
Step 4: Verifying the Installation
To confirm a successful installation, open a new terminal or command prompt and type:
subfinder --version
If Subfinder is correctly installed, it will display the version number. If not, review the installation steps and ensure all prerequisites are met.
Step 5: Customizing Your Setup

Subfinder offers a range of options to customize your subdomain discovery process. By default, Subfinder uses a set of public resolvers, but you can enhance performance and maintain anonymity by using your own resolvers. To do this, create a resolvers.txt file in the subfinder directory and list your resolvers, one per line.
Additionally, Subfinder allows you to specify the number of threads to use for its operations. This can be adjusted using the -t flag, followed by the desired number of threads. For example:
subfinder -d example.com -t 50
This command will run Subfinder with 50 threads on the domain example.com. Adjusting the number of threads can impact performance, so it's advisable to find the optimal value for your system.
Subfinder in Action: A Real-World Example
Let’s walk through a practical example of using Subfinder to discover subdomains. Suppose we want to find all the subdomains associated with the domain example.com.
subfinder -d example.com
Subfinder will begin its discovery process, utilizing various techniques and sources to identify subdomains. The output will list all the discovered subdomains, providing a comprehensive overview of the domain's infrastructure.
For more advanced usage, Subfinder offers additional flags and options. You can specify the output format using the -o flag, choose specific sources to query with the -s flag, and even save the results to a file with the -f flag. For a full list of options, refer to the Subfinder documentation.
Conclusion: Leveraging Subfinder for Security
Subfinder is a powerful tool in the cybersecurity arsenal, offering a comprehensive approach to subdomain discovery. By following this guide, you can seamlessly install Subfinder and customize its settings to suit your needs. With its efficient and accurate subdomain enumeration, Subfinder empowers security professionals and researchers to gain a deeper understanding of domain infrastructure, enhancing their ability to identify potential vulnerabilities and strengthen overall security posture.
What is Subfinder’s role in cybersecurity?
+Subfinder is a tool used for subdomain discovery, a critical step in cybersecurity reconnaissance. By identifying all subdomains associated with a domain, Subfinder helps security professionals and researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s online infrastructure, which is crucial for vulnerability assessment and security enhancement.
How does Subfinder compare to other subdomain discovery tools?
+Subfinder stands out for its efficiency and accuracy in subdomain enumeration. It employs a combination of techniques and sources to ensure comprehensive coverage, making it a preferred choice for many cybersecurity professionals. Additionally, its open-source nature and active community support contribute to its reliability and frequent updates.
Are there any security considerations when using Subfinder?
+While Subfinder is a powerful tool, it’s important to use it responsibly and ethically. Subdomain discovery can reveal sensitive information, so it’s crucial to have the necessary permissions and adhere to legal and ethical guidelines. Additionally, using your own resolvers and adjusting thread counts can enhance security and performance.