Unveiling the Marginal Cost Curve Mystery
Welcome to the world of economics and a deep dive into one of the fundamental concepts that shapes the business landscape: the marginal cost curve. In this comprehensive article, we will unravel the mysteries surrounding this curve, providing you with an in-depth understanding of its significance, characteristics, and impact on various industries. Get ready to embark on an enlightening journey as we explore the intricacies of marginal cost curves and their implications.
Unveiling the Concept: Marginal Cost Curve
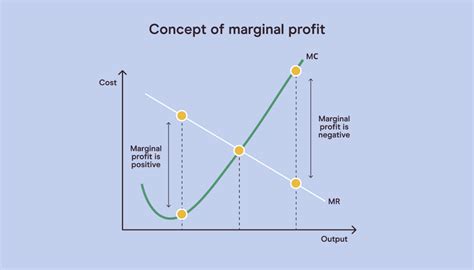
The marginal cost curve is a fundamental tool in microeconomics, offering valuable insights into the relationship between production levels and the associated costs. It represents the additional cost incurred by a firm when producing one additional unit of output. This concept is crucial for businesses as it provides a framework to optimize production decisions, maximize profits, and understand the trade-offs involved.
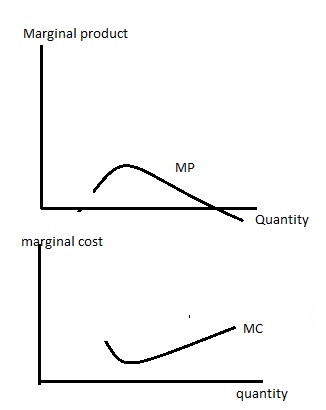
At its core, the marginal cost curve reflects the law of diminishing returns, a fundamental principle in economics. As production increases, the marginal cost initially decreases due to economies of scale. However, beyond a certain point, the marginal cost starts to rise as inefficiencies and constraints kick in. This transition point, where the curve shifts from downward sloping to upward sloping, is a critical juncture for businesses.
Understanding the shape and dynamics of the marginal cost curve is essential for firms to make informed decisions. It enables them to identify the optimal production level, where the marginal cost is minimized, and to assess the impact of various factors such as technology, market conditions, and resource availability on their cost structure.
Key Characteristics of the Marginal Cost Curve
The marginal cost curve exhibits several distinct characteristics that are worth exploring:
- Initial Decrease: At the beginning of production, as output increases, the marginal cost typically declines. This phase represents the economies of scale, where larger production runs lead to cost savings through efficient resource utilization and specialized processes.
- Inflection Point: As production continues, the marginal cost curve reaches an inflection point, where it transitions from a downward slope to an upward slope. This point signifies the optimal production level, where further expansion leads to increasing costs.
- Increasing Costs: Beyond the inflection point, the marginal cost curve slopes upward. This phase reflects the law of diminishing returns, where additional units of output become increasingly costly due to constraints and inefficiencies.
- Variable Factors: The shape of the marginal cost curve is influenced by various factors, including technology, resource availability, market conditions, and production processes. Changes in these variables can shift the curve, impacting the optimal production level and cost structure.
| Factor | Impact on Marginal Cost Curve |
|---|---|
| Technology | Advanced technology can lead to lower marginal costs, as it enables more efficient production processes and reduces resource wastage. |
| Resource Availability | Limited resource availability can increase marginal costs, as firms may need to source resources from alternative, more expensive suppliers. |
| Market Conditions | Fluctuating market demand and pricing can affect the marginal cost curve, as firms may need to adjust production levels to meet market requirements. |
| Production Processes | Inefficient production processes or outdated machinery can result in higher marginal costs, as they require more resources and time to produce each unit. |
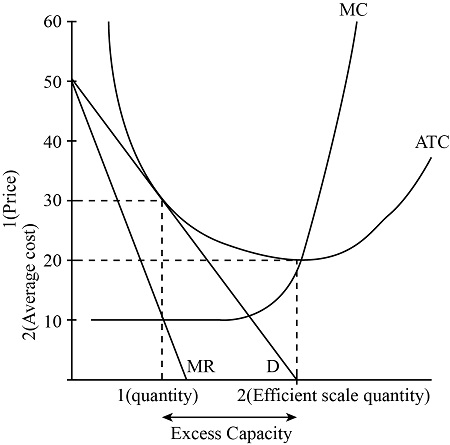
Analyzing the Impact: Implications for Businesses
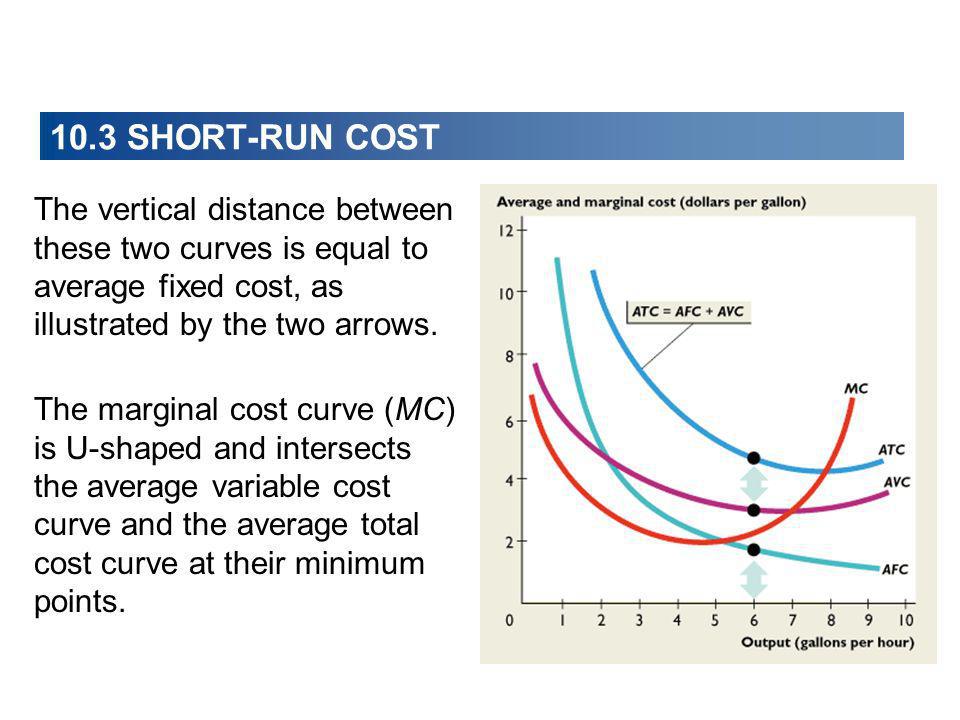
The marginal cost curve holds significant implications for businesses across various industries. By understanding the curve and its dynamics, firms can make strategic decisions to enhance their competitive advantage and optimize their operations.
Cost Optimization and Profit Maximization
One of the primary applications of the marginal cost curve is cost optimization. Businesses can use the curve to identify the production level that minimizes marginal costs, thus maximizing profits. By operating at this optimal point, firms can ensure that their costs are efficiently managed and their profits are maximized.
For instance, consider a manufacturing company that produces widgets. By analyzing its marginal cost curve, the company can determine the production level where the marginal cost is at its lowest. This information allows the company to set its production targets and pricing strategies accordingly, ensuring profitability and market competitiveness.
Decision-Making and Resource Allocation
The marginal cost curve serves as a powerful tool for decision-making and resource allocation. Businesses can use the curve to assess the impact of various production levels on their cost structure. This analysis helps firms make informed choices regarding capacity expansion, investment in new technologies, or adjustments to their production processes.
Imagine a software development firm that offers customized solutions to its clients. By examining its marginal cost curve, the firm can identify the production level where the curve starts to rise, indicating diminishing returns. This information guides the firm in setting project scopes and pricing, ensuring that it avoids overextending its resources and maintains profitability.
Market Strategy and Pricing
The marginal cost curve also plays a crucial role in shaping market strategies and pricing decisions. By understanding the curve, businesses can assess the impact of different production levels on their cost structure and, subsequently, on their pricing. This knowledge allows firms to set competitive prices while maintaining profitability.
Take the example of an e-commerce platform selling a range of products. By analyzing its marginal cost curve, the platform can identify the production levels where the curve starts to slope upward. This information helps the platform determine the optimal pricing strategy, ensuring that it offers competitive prices without compromising its profitability.
Competitive Advantage and Innovation
The marginal cost curve provides insights into the competitive landscape and highlights opportunities for innovation. By comparing their marginal cost curves with those of competitors, businesses can identify areas where they can gain a competitive edge.
Suppose a tech startup develops a new software solution. By comparing its marginal cost curve with those of established competitors, the startup can identify areas where its solution offers cost advantages. This information guides the startup in positioning its product, highlighting its cost-effectiveness and attracting potential customers.
Future Prospects: Evolving with the Marginal Cost Curve
As we conclude our exploration of the marginal cost curve, it is essential to consider its future prospects and the evolving landscape of business and economics.
Technological Advancements and Digital Transformation
The rapid pace of technological advancements and digital transformation is set to influence the marginal cost curve in significant ways. As businesses embrace digital technologies, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics, they can achieve greater efficiency and reduce marginal costs.
For instance, the adoption of robotic process automation (RPA) in manufacturing can lead to increased productivity and reduced labor costs, thus lowering the marginal cost curve. Similarly, the use of predictive analytics in supply chain management can optimize inventory levels, reducing holding costs and further decreasing marginal costs.
Sustainable Practices and Environmental Considerations
With growing awareness and emphasis on sustainability, businesses are increasingly integrating environmentally conscious practices into their operations. These practices can impact the marginal cost curve by introducing additional costs related to sustainable initiatives.
Consider a company that implements energy-efficient technologies in its production processes. While these technologies may initially increase the marginal cost due to the investment required, they can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing energy consumption and associated expenses. Moreover, sustainable practices can enhance a company's reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers, providing a competitive advantage.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Pressures
The dynamic nature of markets and the constant evolution of competitive pressures will continue to shape the marginal cost curve. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, businesses must adapt their strategies and production processes to stay competitive.
In highly competitive industries, firms may face increasing pressure to reduce costs and differentiate their offerings. This can lead to a shift in the marginal cost curve as businesses optimize their operations, innovate, and seek new sources of efficiency. Additionally, market trends and consumer preferences can influence the demand for certain products, further impacting the marginal cost curve.
Regulatory and Policy Changes
Regulatory and policy changes can have significant implications for businesses and their marginal cost curves. Changes in labor laws, environmental regulations, or tax policies can impact a firm's cost structure and, consequently, its marginal cost curve.
For example, stricter environmental regulations may require businesses to invest in new technologies or adopt sustainable practices, leading to increased marginal costs in the short term. However, these changes can also drive innovation and long-term cost savings as businesses adapt to meet regulatory requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the marginal cost curve impact pricing strategies?
+The marginal cost curve plays a crucial role in shaping pricing strategies. By understanding the curve, businesses can determine the production level where the marginal cost is minimized, allowing them to set competitive prices while maximizing profits. This information helps firms strike a balance between cost efficiency and market competitiveness.
Can the marginal cost curve be influenced by external factors?
+Absolutely! The marginal cost curve is influenced by various external factors, including technology, resource availability, market conditions, and production processes. Changes in these factors can shift the curve, impacting the optimal production level and cost structure. Businesses must stay attuned to these external influences to make informed decisions.
How can businesses leverage the marginal cost curve to gain a competitive advantage?
+By analyzing their marginal cost curve and comparing it with competitors, businesses can identify areas where they can gain a competitive edge. This analysis can guide strategic decisions, such as optimizing production processes, investing in new technologies, or developing innovative solutions, to enhance their market position and profitability.
What are the key challenges in understanding and utilizing the marginal cost curve effectively?
+One of the main challenges is accurately estimating the marginal cost curve, as it requires comprehensive data and analysis. Additionally, the dynamic nature of markets and external factors can make it difficult to predict and interpret the curve accurately. Businesses must invest in robust data analytics and stay abreast of market trends to overcome these challenges effectively.
In conclusion, the marginal cost curve is a powerful tool that businesses can leverage to optimize their operations, maximize profits, and gain a competitive advantage. By understanding its characteristics, implications, and future prospects, firms can navigate the complex business landscape with confidence and success.