Say Goodbye to Blank Cells: Excel's Formula Fix
Excel, a powerful tool used by professionals and individuals worldwide, is renowned for its ability to streamline data analysis and management. However, one common challenge that Excel users face is dealing with blank cells within their datasets. Blank cells can disrupt the integrity of calculations, pivot tables, and visualizations, leading to inaccurate results and misinterpretations. In this article, we delve into the world of Excel formulas, exploring effective strategies to conquer blank cells and unlock the full potential of your data analysis.
Understanding the Impact of Blank Cells

Blank cells in Excel can be unintentional, arising from data entry errors, missing information, or deliberate omissions. Regardless of their origin, these empty spaces can have significant consequences for your analysis. When performing calculations or aggregating data, Excel often excludes blank cells, potentially skewing the results. For instance, consider a simple average calculation where one value is missing. The formula, when applied, will yield an incorrect average, affecting the accuracy of your analysis.
Additionally, blank cells can impact the functionality of Excel's powerful features like pivot tables and conditional formatting. These tools rely on complete and consistent data to deliver accurate insights. When faced with blank cells, they may produce unexpected results or fail to function as intended, hindering your ability to extract meaningful information from your dataset.
Strategies to Conquer Blank Cells

To mitigate the impact of blank cells and ensure accurate analysis, Excel provides a range of powerful tools and techniques. Here are some strategies to address this common challenge:
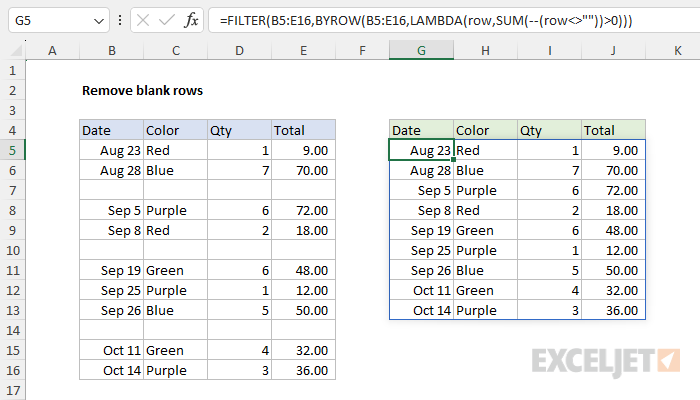
1. Understanding Blank Cell Treatment in Formulas
Excel offers several options for dealing with blank cells in formulas. By default, Excel excludes blank cells from calculations, but you can customize this behavior using the IF function. The IF function allows you to specify alternative values or actions for blank cells, ensuring more accurate results. For instance, you can replace blank cells with a zero, a specific value, or even a custom message to provide context to your calculations.
Consider the following example:
| Product | Sales |
|---|---|
| Widget A | 100 |
| Widget B | 50 |
| Widget C |

To calculate the total sales, you can use the SUM function, but the presence of a blank cell will affect the result. By utilizing the IF function, you can replace the blank cell with a specific value. For instance, =SUM(IF(ISBLANK(A2:A4), 0, A2:A4)) will sum the values in column A, treating blank cells as zeros.
2. Utilizing Excel’s Data Validation Tools
Excel’s data validation tools provide an effective way to prevent blank cells from occurring in the first place. By setting up data validation rules, you can ensure that cells contain valid data and avoid accidental omissions. For example, you can create a rule that requires a value to be entered in a cell before moving on to the next one.
To set up data validation, follow these steps:
- Select the range of cells you want to validate.
- Go to the Data tab and click on Data Validation.
- In the Data Validation dialog box, choose the Custom option and enter a formula that defines the validation criteria.
- For example, you can use the formula =NOT(ISBLANK(A1)) to ensure that cell A1 is not blank.
By implementing data validation, you can prompt users to input data and prevent blank cells from appearing in your dataset.
3. Handling Blank Cells in Pivot Tables
Pivot tables are a powerful feature in Excel that allows you to summarize and analyze large datasets. However, blank cells can impact the accuracy of your pivot table results. To address this issue, Excel provides the Show Values As feature, which allows you to customize how blank cells are treated.
When creating a pivot table, right-click on a value cell and select Value Field Settings. In the Show Values As section, you can choose options like Show All to include blank cells or Show Data as Text to treat blank cells as text values.
By utilizing these settings, you can ensure that blank cells are handled appropriately and do not affect the accuracy of your pivot table analysis.
4. Conditional Formatting for Blank Cell Identification
Conditional formatting is a valuable tool in Excel that allows you to visually identify and highlight cells based on specific criteria. This feature can be particularly useful for identifying blank cells within your dataset.
To apply conditional formatting to blank cells, follow these steps:
- Select the range of cells you want to format.
- Go to the Home tab and click on Conditional Formatting.
- Choose New Rule and select the Format only cells that contain option.
- In the Edit the Rule Description section, choose Blanks from the drop-down menu.
- Apply your desired formatting, such as a specific color or font style, to highlight the blank cells.
By using conditional formatting, you can quickly identify blank cells and take appropriate action, such as filling in missing data or applying custom formulas.
Conclusion
Blank cells in Excel can be a nuisance, but with the right strategies and tools, you can conquer them and ensure accurate data analysis. By understanding how Excel treats blank cells in formulas, utilizing data validation, customizing pivot table settings, and applying conditional formatting, you can take control of your dataset and produce reliable results.
Remember, accurate data analysis is crucial for making informed decisions and deriving meaningful insights. By addressing the issue of blank cells, you can enhance the integrity of your Excel workbooks and unlock the full potential of this powerful software.
FAQ
Can I automatically fill in blank cells with a specific value in Excel?
+
Yes, you can use the IF function in combination with the ISBLANK function to automatically fill in blank cells with a specific value. For example, =IF(ISBLANK(A1), “N/A”, A1) will display “N/A” in any blank cells in column A.
How can I prevent blank cells from appearing in my Excel data validation rules?
+
You can use the Data Validation feature in Excel to create custom rules that prevent blank cells. For instance, you can set a rule that requires a value to be entered before a cell is considered valid. This ensures that users input data and prevents blank cells from appearing.
What happens if I don’t address blank cells in my Excel calculations?
+
If you don’t address blank cells in your calculations, Excel will typically exclude them from the results. This can lead to inaccurate calculations and misinterpretations of your data. It’s important to handle blank cells appropriately to ensure accurate analysis.
Are there any Excel add-ins or tools that can help with managing blank cells?
+
Yes, there are several Excel add-ins and tools available that can assist with managing blank cells. These tools offer advanced features, such as bulk filling of blank cells or identifying patterns in missing data. Some popular options include the Power Query add-in and specialized blank cell management tools.
Can I use conditional formatting to highlight specific types of blank cells in Excel?
+
Absolutely! Conditional formatting in Excel allows you to highlight specific types of blank cells based on your criteria. For example, you can format cells that are blank but should contain a value, or identify cells that are blank due to a formula error. This helps you quickly identify and address different types of blank cells.



