Unraveling Stem and Leaf Plots
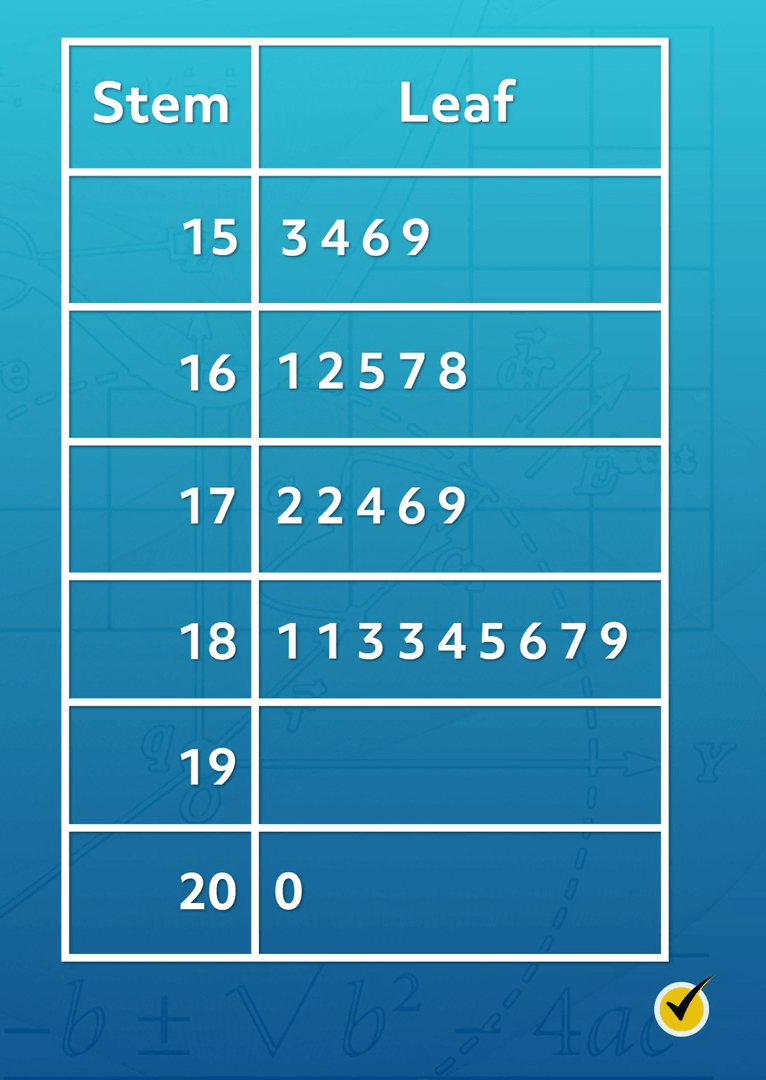
The concept of stem and leaf plots is an intriguing aspect of data visualization, offering a simple yet effective way to represent and understand numerical data. This method, a classic in the field of statistics and data science, provides a unique perspective on datasets, making it an essential tool for analysts and researchers. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of stem and leaf plots, exploring their construction, interpretation, and applications in various fields.
Understanding Stem and Leaf Plots: A Comprehensive Overview

A stem and leaf plot, also known as a stemplot, is a visual representation of data that organizes and displays numerical values in a clear and concise manner. It is particularly useful for small to moderate-sized datasets, providing an efficient way to analyze and communicate data distribution. The beauty of this plot lies in its simplicity, as it transforms raw data into a structured format, making patterns and trends easily discernible.
At its core, a stem and leaf plot consists of two main components: the stem, which represents the first digit(s) of the data points, and the leaves, which represent the remaining digits. This division allows for a hierarchical arrangement of data, where similar values are grouped together, facilitating the identification of clusters, outliers, and other important data characteristics.
Constructing a Stem and Leaf Plot
Constructing a stem and leaf plot involves a systematic process that transforms raw data into a visually organized format. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building a stem and leaf plot:
- Data Collection: Gather the numerical data you wish to analyze and organize it in ascending or descending order. This step is crucial as it ensures that similar values are grouped together.
- Identify Stems and Leaves: Determine the number of digits your data points have. The leftmost digit(s) will form the stem, while the remaining digits will become the leaves.
- Create the Stem Column: Start by writing the unique values of the stem digits in a column. These values should be arranged in ascending or descending order, depending on the preferred data arrangement.
- Add the Leaf Values: For each stem value, write the corresponding leaf values to its right. Ensure that the leaf values are listed in ascending order for each stem.
- Format the Plot: Adjust the spacing and formatting of your plot to enhance readability. You can use vertical lines or spaces to separate stems and leaves, making it easier to scan the data.
For instance, consider the following dataset: [23, 45, 56, 67, 78, 89, 90]. To create a stem and leaf plot, we would identify the stem as the tens digit (2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) and the leaf as the units digit (3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0). The plot would look like this:
| Stem | Leaf |
|---|---|
| 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 7 |
| 7 | 8 |
| 8 | 9 |
| 9 | 0 |

Interpreting Stem and Leaf Plots
Interpreting a stem and leaf plot involves analyzing the arrangement of data to extract meaningful information. Here are some key aspects to consider when interpreting a stemplot:
- Data Distribution: The plot provides a clear view of the data's spread. You can quickly identify the range of values, the most common values (modes), and any gaps or clusters in the data.
- Outliers and Anomalies: Stem and leaf plots are excellent for spotting outliers - values that are significantly higher or lower than the majority of the data. These outliers often stand out as lone leaves or small clusters, indicating unusual data points.
- Data Clustering: The plot reveals natural groupings or clusters in the data. This is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets, as it helps identify patterns and potential subsets within the data.
- Symmetry and Skewness: By examining the plot's shape, you can determine if the data is symmetric (bell-shaped), skewed to the left (negative skew), or skewed to the right (positive skew). This information is vital for understanding the data's distribution and making statistical inferences.
Applications of Stem and Leaf Plots

Stem and leaf plots find applications across various fields, offering a simple yet powerful tool for data analysis and communication. Here are some areas where stem and leaf plots are particularly valuable:
Education and Teaching
Stem and leaf plots are a staple in mathematics and statistics education. They provide a visual tool for students to understand data distribution, identify patterns, and develop analytical skills. By constructing and interpreting stemplots, students gain a deeper understanding of numerical data and its characteristics.
Research and Analysis
Researchers and analysts across disciplines, from biology to economics, use stem and leaf plots to visualize and analyze their data. These plots offer a quick and effective way to summarize and present data, making it easier to communicate findings and identify key trends. For instance, in biology, stem and leaf plots can be used to visualize the distribution of plant heights or animal weights, aiding in ecological studies.
Quality Control and Process Monitoring
In manufacturing and quality control, stem and leaf plots are used to monitor production processes and identify potential issues. By plotting data such as product dimensions or test results, analysts can quickly identify variations and outliers, ensuring that the process remains within acceptable limits.
Data Exploration and Initial Analysis
Before delving into complex statistical methods, stem and leaf plots provide an initial, exploratory look at the data. They offer a quick way to understand the data’s distribution, identify any unusual values, and make informed decisions about further analysis.
Future Implications and Advancements
While stem and leaf plots have been a staple in data visualization for decades, they continue to evolve and find new applications. With the advancement of technology and data science, stem and leaf plots can now be easily created and customized using various software and programming languages. This accessibility has made stemplots a go-to tool for data professionals, educators, and enthusiasts alike.
Furthermore, the integration of stem and leaf plots with other data visualization techniques, such as box plots and histograms, provides a comprehensive toolkit for data analysis. By combining these methods, analysts can gain a deeper understanding of their data and make more informed decisions.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the world of stem and leaf plots, uncovering their construction, interpretation, and applications. As a simple yet powerful tool, stem and leaf plots offer a unique perspective on numerical data, aiding in its understanding and communication. Whether in education, research, or industry, stem and leaf plots continue to be a valuable asset for data professionals and enthusiasts.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the benefits of using stem and leaf plots over other data visualization methods?
+
Stem and leaf plots offer a simple and intuitive way to visualize data, making it easy to identify patterns and outliers. They provide a quick overview of the data’s distribution, making them ideal for initial data exploration and analysis. Additionally, their hierarchical structure makes it straightforward to understand the relationship between different data points.
Can stem and leaf plots be used for large datasets?
+
While stem and leaf plots are most effective for small to moderate-sized datasets, they can still provide valuable insights for larger datasets. By using a representative sample or dividing the data into subsets, you can create stem and leaf plots that offer a meaningful overview of the data’s distribution and characteristics.
Are there any limitations to using stem and leaf plots?
+
One limitation of stem and leaf plots is that they are less effective for continuous data with a wide range of values. In such cases, other visualization methods like histograms or box plots may provide a better representation. Additionally, stem and leaf plots may not be the best choice for datasets with a large number of outliers, as these outliers can dominate the plot and make it difficult to interpret.