The Complete Guide to Population Pyramids
Welcome to the ultimate guide on understanding and interpreting population pyramids, an essential tool for demographers, policymakers, and anyone interested in exploring the intricate dynamics of human populations. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the various aspects of population pyramids, from their basic structure to their profound implications for society and future planning.
Population pyramids, or age-sex pyramids, are visual representations of a population's age and gender structure at a specific point in time. These diagrams offer a powerful lens through which we can examine the demographic characteristics of a given population, providing valuable insights into its current and future state.
By visually presenting the distribution of a population across different age groups, population pyramids reveal critical information about birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, and overall population trends. This information is not only crucial for understanding the present but also for predicting and planning for the future, making it an indispensable tool for policymakers, researchers, and social planners.
Understanding the Basics of Population Pyramids
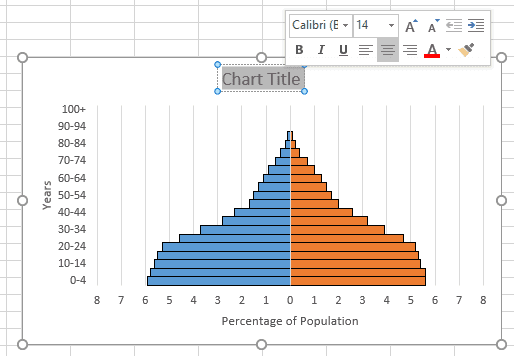
At its core, a population pyramid is a simple yet powerful graphical representation. It consists of two symmetrical bars, one for males and one for females, divided into age groups. These age groups are typically represented in five-year intervals, with the youngest age group at the bottom and the oldest at the top.
The width of each bar segment represents the size of the population in that particular age group and gender. A broader base indicates a larger population of young individuals, while a narrow top represents a smaller population of older individuals. This visual representation allows us to quickly grasp the demographic makeup of a population and identify any notable trends or patterns.
Interpreting the Shape of Population Pyramids
The shape of a population pyramid can vary significantly, reflecting the unique characteristics and dynamics of a population. Three primary shapes are commonly recognized, each with its own set of implications:
- Expanding Population Pyramids: This pyramid has a broad base, representing a large number of births and a young population. The sides of the pyramid gradually taper inwards as the population ages, resulting in a pyramid shape. This type of pyramid often indicates a high birth rate and a rapidly growing population. Countries experiencing economic development and social changes often exhibit this pyramid shape.
- Stable Population Pyramids: In contrast, a stable population pyramid has a more symmetrical shape, with a relatively even distribution of population across different age groups. The base and top of the pyramid are roughly equal in width, indicating a balanced birth and death rate. This pyramid shape suggests a population that is neither growing nor shrinking significantly.
- Contracting Population Pyramids: A contracting pyramid has a narrow base and a wider top, indicating a smaller number of births and a larger proportion of older individuals. This shape often reflects a low birth rate and an aging population. Countries with advanced healthcare and social security systems, as well as those facing economic challenges, may exhibit this pyramid shape.
Key Metrics and Trends in Population Pyramids
Population pyramids offer a wealth of information beyond their basic structure. By analyzing specific metrics and trends, we can gain deeper insights into a population’s health, social dynamics, and future prospects.
Age Structure and Dependency Ratios
The age structure of a population pyramid provides valuable insights into the distribution of individuals across different age groups. This information is crucial for understanding the dependency ratios within a population. Dependency ratios measure the ratio of individuals who are typically dependent on others (children and older adults) to those who are typically economically active (working-age adults). A high dependency ratio can strain a country’s resources and social welfare systems, while a low ratio can indicate a productive and sustainable population.
A country's dependency ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
| Dependency Ratio | = | (Population under 15 years old + Population over 64 years old) / Population aged 15-64 years old |
|---|
For example, if a country has a population of 100 million, with 20 million people under 15 years old, 50 million people aged 15-64, and 30 million people over 64 years old, the dependency ratio would be:
| (20 million + 30 million) / 50 million | = | 0.8 |
This means that for every 100 working-age adults, there are 80 dependent individuals. A high dependency ratio can have significant implications for a country's economy and social welfare programs.
Life Expectancy and Health Trends
Population pyramids also provide insights into life expectancy and overall health trends within a population. By examining the survival rates of different age groups, we can assess the effectiveness of healthcare systems and the impact of various health initiatives. For instance, a pyramid with a large proportion of individuals reaching advanced ages may indicate successful healthcare interventions and improved life expectancy.
Additionally, the shape of the pyramid can reveal gender-specific health disparities. If one gender consistently has a higher mortality rate at certain ages, it could point to specific health issues or social factors that need to be addressed.
Migration and Fertility Patterns
Population pyramids can offer clues about migration patterns and fertility rates. A sudden change in the shape of a pyramid, especially in the younger age groups, may indicate significant migration events or shifts in fertility rates. For instance, a sharp increase in the number of young individuals could be a result of migration or a baby boom, while a decline might suggest outmigration or declining fertility rates.
The Impact of Population Pyramids on Society and Planning
Population pyramids are not just static representations; they have profound implications for society and future planning. Understanding the demographic trends revealed by population pyramids can help policymakers and planners make informed decisions in various sectors, including healthcare, education, infrastructure, and social welfare.
Healthcare and Social Welfare Planning
The age structure of a population pyramid is particularly crucial for healthcare planning. As populations age, the demand for healthcare services, particularly for chronic diseases and geriatric care, increases. By analyzing population pyramids, healthcare systems can anticipate future needs, plan for resource allocation, and develop strategies to meet the changing healthcare demands of an aging population.
Similarly, population pyramids can guide social welfare planning. A pyramid with a large proportion of elderly individuals may require adjustments in pension systems and social security programs to ensure financial sustainability. On the other hand, a pyramid with a large youth population may necessitate investments in education and employment opportunities to support future economic growth.
Economic and Infrastructure Development
Population pyramids also play a significant role in economic planning and infrastructure development. A growing population, indicated by an expanding pyramid, may require investments in housing, transportation, and other essential services. On the other hand, a contracting pyramid may lead to different infrastructure needs, such as retirement homes and elderly care facilities.
Furthermore, the age structure of a population can impact labor force participation and productivity. A pyramid with a large working-age population can be a significant asset for economic growth, while a pyramid with a small working-age population may require innovative solutions to maintain economic vitality.
Educational and Social Policies
Population pyramids can inform educational policies and social programs. For instance, a pyramid with a large number of young children may require investments in early childhood education and childcare facilities. Conversely, a pyramid with a large youth population may necessitate investments in higher education and vocational training to prepare them for the job market.
Additionally, population pyramids can guide social policies aimed at promoting gender equality and addressing gender-specific health and social issues. By identifying gender disparities in mortality rates or life expectancy, policymakers can develop targeted interventions to improve health outcomes and social conditions for all individuals.
Future Trends and Implications
As global populations continue to evolve, population pyramids will remain a vital tool for understanding and predicting demographic changes. With advancements in healthcare and improvements in living standards, life expectancy is increasing, leading to a growing proportion of elderly individuals in many countries. This trend has significant implications for healthcare systems, pension funds, and social welfare programs.
Additionally, changing social norms and economic factors are influencing fertility rates and migration patterns. These changes can lead to shifts in population pyramids, with potential consequences for a country's economic growth, social fabric, and overall well-being. Understanding these future trends and their potential impacts is crucial for effective planning and policy-making.
In conclusion, population pyramids are powerful tools that offer a wealth of information about a population's past, present, and future. By understanding and interpreting these pyramids, we can gain valuable insights into demographic trends, plan for future challenges, and make informed decisions to ensure a sustainable and prosperous society.
How often should population pyramids be updated to remain accurate and relevant?
+Population pyramids should ideally be updated annually to capture the most recent demographic changes. However, in some cases, updates may be done more frequently, especially if there are significant events or policies that could impact the population structure. For long-term planning, a minimum of every five years is recommended.
What are some common challenges or limitations when using population pyramids for analysis?
+One challenge is the assumption of constant fertility, mortality, and migration rates over time, which may not always hold true. Additionally, population pyramids provide a snapshot of a population at a specific moment, so they may not capture short-term fluctuations or temporary changes. It’s important to consider these limitations when interpreting the data.
Can population pyramids be used to predict future population growth or decline accurately?
+While population pyramids can provide valuable insights into demographic trends, they are not foolproof predictors of future population growth or decline. Unforeseen events, policy changes, and social factors can influence these trends. However, by analyzing population pyramids alongside other demographic data and trends, more accurate predictions can be made.