Hormones and Enzymes: Unveiling Their Unique Roles
Hormones and enzymes are two fundamental components of biological systems, playing distinct and crucial roles in maintaining the intricate balance of life. From regulating growth and development to facilitating essential biochemical reactions, their unique functions are indispensable to the functioning of all living organisms. In this article, we will delve into the specific roles of hormones and enzymes, highlighting their individual contributions and the fascinating interplay that exists between them.
The Orchestrators: Hormones and Their Dynamic Functions
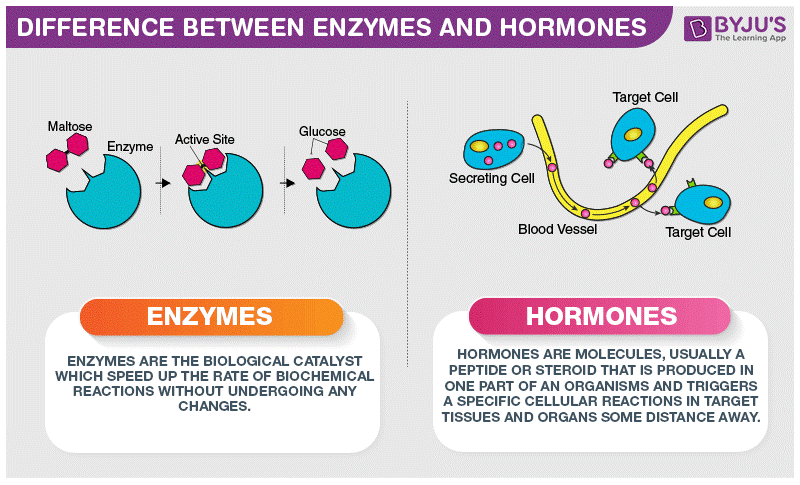
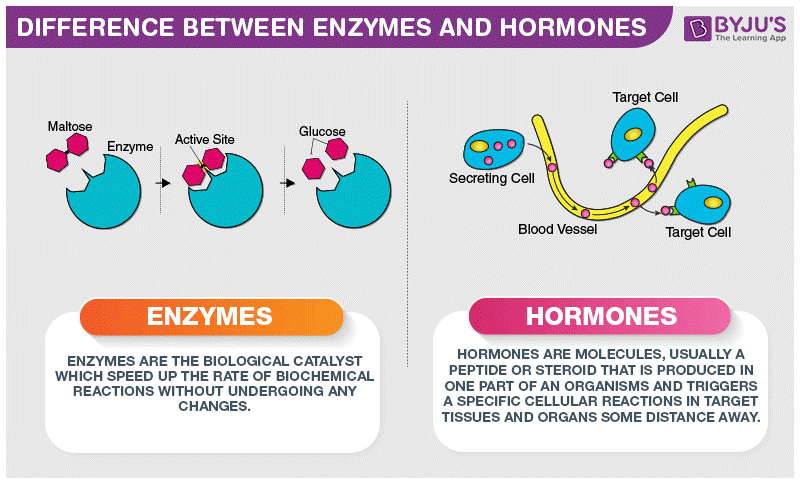
Hormones are biochemical messengers that act as the body’s conductors, orchestrating a wide array of physiological processes. These remarkable molecules, secreted by various glands and organs, travel through the bloodstream to target specific tissues or organs, where they exert their regulatory influence. The diversity of hormones is reflected in the myriad of functions they perform, each with its own unique impact on the body’s homeostasis.
Growth and Development: The Master Regulators
Hormones are the key players in the intricate process of growth and development. From the early stages of embryonic development to the attainment of maturity, hormones guide the body’s growth, shaping its physical and functional characteristics. The growth hormone, for instance, plays a pivotal role in promoting cell growth and regeneration, while sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone orchestrate the development of secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive functions.
The impact of hormones on growth is evident in conditions like gigantism, where an excess of growth hormone leads to abnormal height, and dwarfism, where a deficiency in growth hormone results in stunted growth. Similarly, imbalances in sex hormones can lead to developmental disorders, underscoring the critical role hormones play in ensuring the body's proper growth and development.
Metabolism and Energy Balance: Hormonal Fine-Tuning
Hormones also play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, the complex network of biochemical reactions that sustain life. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, is a prime example. It acts as a key regulator of glucose metabolism, promoting the uptake of glucose by cells and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Conversely, glucagon, another pancreatic hormone, works in opposition to insulin, stimulating the release of glucose from storage when blood sugar levels drop.
The delicate balance between these two hormones is essential for maintaining energy homeostasis. Disruptions in this balance can lead to metabolic disorders such as diabetes, where either an insufficient production or an impaired response to insulin results in elevated blood sugar levels.
Hormonal Communication: Signaling Networks
Hormones communicate with target cells through intricate signaling pathways. This communication is highly specific, with each hormone binding to its unique receptor on the cell surface. The activation of these receptors triggers a cascade of intracellular events, ultimately leading to the desired physiological response. For instance, the hormone melatonin, produced by the pineal gland, binds to its receptors in the brain, regulating sleep-wake cycles and maintaining circadian rhythm.
The Catalysts: Enzymes and Their Biochemical Prowess

Enzymes, often referred to as biological catalysts, are indispensable for life. These protein-based molecules facilitate and accelerate biochemical reactions, playing a central role in virtually every biochemical process within the body. Their ability to lower the activation energy required for reactions is a cornerstone of life’s efficiency and complexity.
Catalytic Powerhouses: Speeding Up Reactions
Enzymes are remarkably efficient catalysts, often increasing reaction rates by millions of times. This catalytic prowess is achieved through a precise fit between the enzyme’s active site and the substrate it acts upon. The enzyme-substrate complex forms a temporary structure, lowering the energy barrier for the reaction to occur. Once the reaction is complete, the enzyme is released, ready to catalyze another reaction.
The specificity of enzymes is a key feature. Each enzyme is highly specific for its substrate, ensuring that biochemical reactions occur in a controlled and directed manner. This specificity is vital for maintaining the body's intricate biochemical pathways, allowing for the precise regulation of metabolic processes.
Metabolic Pathways: Enzymatic Control
Enzymes are the master regulators of metabolic pathways, the interconnected series of biochemical reactions that sustain life. They control the flow of reactions, determining the rate at which substrates are converted into products. For instance, in the citric acid cycle, a central pathway for energy production, enzymes like citrate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyze specific reactions, ensuring the efficient conversion of substrates into energy-rich molecules.
| Enzyme | Function |
|---|---|
| Citrate Synthase | Catalyzes the formation of citrate, a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle. |
| Isocitrate Dehydrogenase | Converts isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate, releasing CO2 and producing NADH, an energy-rich molecule. |

Enzymatic Regulation: Feedback Loops
Enzymes are subject to intricate regulatory mechanisms, often involving feedback loops. In these loops, the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor for an enzyme earlier in the pathway, thus controlling the overall rate of the pathway. This self-regulating mechanism ensures that the body’s metabolic processes remain balanced and efficient.
The Interplay: Hormones and Enzymes in Concert
While hormones and enzymes have distinct roles, their functions are intricately intertwined. Hormones often act as master regulators, initiating or modulating metabolic pathways, while enzymes facilitate these processes by catalyzing the necessary biochemical reactions. This interplay is best exemplified in the regulation of blood sugar levels.
Hormonal-Enzymatic Regulation of Blood Sugar
The regulation of blood sugar levels is a complex process involving both hormones and enzymes. When blood sugar levels rise, as after a meal, the pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin binds to its receptors on liver and muscle cells, triggering a series of intracellular events that lead to the activation of specific enzymes. These enzymes facilitate the uptake and storage of glucose, lowering blood sugar levels back to normal.
Conversely, when blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas secretes glucagon. Glucagon binds to its receptors, leading to the activation of enzymes that break down glycogen (the stored form of glucose) into glucose, thus raising blood sugar levels.
Hormone-Enzyme Interactions: A Complex Web
The interaction between hormones and enzymes extends beyond blood sugar regulation. Many hormones exert their effects by modulating the activity of specific enzymes. For instance, thyroid hormones regulate the activity of numerous enzymes involved in energy metabolism, while steroid hormones influence the activity of enzymes involved in gene expression.
The interplay between hormones and enzymes is a finely tuned process, ensuring the body's physiological processes remain balanced and efficient. Disruptions in this delicate balance can lead to a host of disorders, highlighting the critical importance of this intricate hormonal-enzymatic network.
Conclusion: The Unwavering Importance of Hormones and Enzymes
Hormones and enzymes are the unsung heroes of biological systems, each playing an indispensable role in the complex symphony of life. From the regulation of growth and metabolism to the facilitation of essential biochemical reactions, their unique functions are vital to the health and well-being of all living organisms. Understanding their roles and the intricate interplay that exists between them provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of life itself.
How do hormones influence growth and development in organisms?
+Hormones are master regulators of growth and development, guiding the body’s physical and functional characteristics. They play a pivotal role in embryonic development, the attainment of maturity, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Imbalances in hormones can lead to developmental disorders, emphasizing their critical role in growth.
What is the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways?
+Enzymes are master regulators of metabolic pathways, controlling the flow of reactions and determining the rate at which substrates are converted into products. They facilitate the efficient conversion of substrates into energy-rich molecules, ensuring the body’s intricate biochemical pathways remain balanced and functional.
How do hormones and enzymes interact to regulate blood sugar levels?
+Hormones and enzymes work in concert to regulate blood sugar levels. When blood sugar rises, insulin is secreted, binding to receptors and activating enzymes that facilitate glucose uptake and storage. Conversely, when blood sugar drops, glucagon is secreted, activating enzymes that break down glycogen into glucose, thus raising blood sugar levels.