Mastering VLOOKUP: Multiple Criteria in Google Sheets
In the world of data analysis and spreadsheet management, the VLOOKUP function is a powerful tool that has become a staple for many professionals. However, what happens when you need to perform lookups based on multiple criteria? This article will delve into the art of mastering VLOOKUP with multiple criteria in Google Sheets, offering a comprehensive guide to enhance your data manipulation skills.
Understanding VLOOKUP with Multiple Criteria

The VLOOKUP function in Google Sheets is a versatile tool designed to search for a value in the leftmost column of a table and return a value from the same row in a specified column. While it is a powerful tool for single-criterion lookups, its true potential lies in handling multiple criteria, allowing you to perform complex data retrievals with ease.
By incorporating multiple criteria into your VLOOKUP formula, you can effectively search and match specific conditions, providing more accurate and granular results. This technique is especially valuable when dealing with large datasets or when you need to filter data based on multiple parameters.
Setting Up the Data for Multiple Criteria VLOOKUP

Before diving into the intricacies of the formula, it’s crucial to organize your data in a structured manner. Here’s a breakdown of the steps to set up your data for multiple criteria VLOOKUP:
Step 1: Define the Lookup Table
Identify the table or range of cells that will serve as your lookup table. This table should contain the data you want to search and retrieve. Ensure that the data is organized logically, with the lookup value in the leftmost column and the desired return value in a column to its right.
Step 2: Prepare the Criteria Range
Create a separate range of cells that will hold the criteria you want to match. These cells should contain the values or conditions you wish to use as filters. For instance, if you’re looking up customer data based on their names and ages, create a range with two columns: one for names and another for ages.
Step 3: Organize the Return Range
Determine the range of cells where you want the VLOOKUP function to return the desired values. This range should be in the same table as the lookup table, but it can be in any column to the right of the lookup value column.
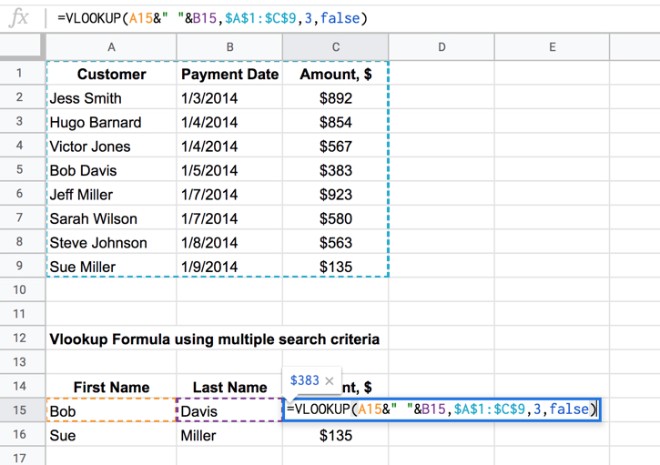
The Multiple Criteria VLOOKUP Formula
Now, let’s construct the formula for a VLOOKUP with multiple criteria. The formula follows a specific structure, which we’ll break down into steps:
Step 1: Define the Lookup Value
Start by identifying the lookup value, which is the value you want to search for in the leftmost column of your lookup table. This can be a cell reference or a literal value. For example, if you’re searching for a customer’s name, you might use =VLOOKUP(B2, …)
Step 2: Specify the Lookup Table
Next, provide the range of cells that constitute your lookup table. This is the table where the VLOOKUP function will search for the lookup value. Ensure that you include the entire table, including the headers if they exist. For instance, if your lookup table is on Sheet1, you might use =VLOOKUP(B2, Sheet1!A2:C20, …)
Step 3: Determine the Return Column
Choose the column number from your lookup table where you want the VLOOKUP function to return the desired value. This is specified as the third argument in the formula. Remember that the column numbers start with 1, so if you want to return the value from the second column, you would use 2. For example, =VLOOKUP(B2, Sheet1!A2:C20, 2, …)
Step 4: Set the Range Lookup
The range lookup is an optional argument that specifies whether you want an exact or approximate match. For multiple criteria VLOOKUP, it’s recommended to set this to FALSE for an exact match. This ensures that the function returns the correct value only when all criteria are met. So, your formula would look like this: =VLOOKUP(B2, Sheet1!A2:C20, 2, FALSE)
Step 5: Incorporate the Multiple Criteria
Now, the key to mastering multiple criteria VLOOKUP lies in this step. You need to use the ARRAYFORMULA function to combine multiple criteria into a single array. The ARRAYFORMULA function allows you to perform calculations on an array of values, which is perfect for handling multiple conditions. Here’s how you can incorporate it:
Let's assume you have two criteria: the customer's name in B2 and their age in C2. Your formula would look like this:
=ARRAYFORMULA(VLOOKUP(B2:C2, Sheet1!A2:C20, 3, FALSE))
In this formula, B2:C2 represents the range of cells containing your criteria, and Sheet1!A2:C20 is the lookup table. The number 3 specifies the column from which you want to return the value. The FALSE argument ensures an exact match.
Tips and Tricks for Effective Multiple Criteria VLOOKUP
Here are some additional tips to make your multiple criteria VLOOKUP even more efficient and accurate:
- Use Absolute References: When dealing with large datasets, it's essential to use absolute references to lock specific cells or ranges. This ensures that your formula remains consistent even when copying it to other cells.
- Sort Your Data: Sorting your lookup table can significantly improve the efficiency of your VLOOKUP. By ensuring that the leftmost column is sorted, you can take advantage of the function's ability to perform approximate matches, which can be faster for large datasets.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: It's common to encounter errors when working with VLOOKUP, especially when criteria are not met. You can use the IFERROR function to handle these gracefully. For instance, you can return a custom message or a default value when the criteria are not satisfied.
- Combine with Other Functions: VLOOKUP is a powerful tool, but it can be even more versatile when combined with other functions like INDEX and MATCH. These functions can help you perform more complex lookups and retrievals.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies

Multiple criteria VLOOKUP has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are a few real-world scenarios where this technique can be invaluable:
Scenario 1: Customer Data Analysis
Imagine you’re a data analyst for an e-commerce company, and you need to analyze customer data to identify high-value customers. By using multiple criteria VLOOKUP, you can search for customers based on their purchase history, average order value, and frequency of purchases. This allows you to segment your customer base effectively and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Scenario 2: Inventory Management
In a retail context, managing inventory is crucial. With multiple criteria VLOOKUP, you can efficiently track inventory levels based on product categories, suppliers, and locations. This helps you optimize your stock levels, identify slow-moving items, and ensure timely reorders.
Scenario 3: Financial Reporting
Financial analysts often need to consolidate data from multiple sources. By using multiple criteria VLOOKUP, they can merge financial data based on account numbers, transaction dates, and specific categories. This simplifies the process of creating accurate and comprehensive financial reports.
Future Implications and Best Practices
As data becomes increasingly complex and voluminous, the ability to perform efficient lookups and retrievals is more critical than ever. Here are some future implications and best practices to consider when working with multiple criteria VLOOKUP:
- Data Integrity: Ensure that your data is clean and well-organized. Inconsistent or incorrect data can lead to inaccurate results and misinterpretations.
- Performance Optimization: When dealing with large datasets, consider using INDEX and MATCH instead of VLOOKUP for improved performance. These functions can handle complex lookups more efficiently.
- Continuous Learning: Google Sheets is constantly evolving, and new functions and features are introduced regularly. Stay updated with the latest advancements to enhance your data manipulation skills.
- Documentation and Collaboration: Document your formulas and methodologies to ensure consistency and facilitate collaboration. Well-documented spreadsheets are invaluable when working in teams or when sharing data with others.
Conclusion
Mastering VLOOKUP with multiple criteria is a powerful skill that can revolutionize the way you analyze and manipulate data in Google Sheets. By understanding the intricacies of this technique and applying it effectively, you can streamline your data analysis processes and make more informed decisions. As you continue to explore and experiment with this powerful tool, you’ll unlock new possibilities and take your data management skills to the next level.
How can I handle multiple criteria with more than two conditions?
+To handle multiple criteria with more than two conditions, you can use the same approach by expanding the range of cells in your ARRAYFORMULA. For example, if you have three criteria (name, age, and gender), you would use a range like B2:C2:D2. Ensure that your lookup table includes all the necessary columns to match these criteria.
Can I use multiple criteria VLOOKUP for dynamic data ranges?
+Yes, you can use multiple criteria VLOOKUP with dynamic data ranges. You can achieve this by using functions like OFFSET or INDIRECT to dynamically adjust the lookup table range based on the data available. This ensures that your formula adapts to changes in the dataset.
What if my criteria are in different sheets or workbooks?
+If your criteria are in different sheets or workbooks, you can still use multiple criteria VLOOKUP. Simply reference the appropriate cells or ranges using sheet or workbook names. For example, =VLOOKUP(Sheet2!B2:C2, Sheet1!A2:C20, 3, FALSE) would allow you to match criteria from Sheet2 with data from Sheet1.
How can I handle situations where an exact match is not found?
+If you want to handle situations where an exact match is not found, you can use the IFERROR function in combination with your VLOOKUP formula. For example, you can return a custom message or a default value when the criteria are not met. This helps prevent errors and provides a more user-friendly experience.



