How to Use Conditional Formatting in Google Sheets
Google Sheets is a powerful tool for data analysis and visualization, and conditional formatting is one of its most useful features. This feature allows you to highlight and format your data based on specific conditions or rules, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within your dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of conditional formatting in Google Sheets, covering everything from the basics to advanced techniques.
Understanding Conditional Formatting

Conditional formatting is a technique that applies formatting changes to your data cells based on certain criteria. These criteria can be defined using formulas or predefined rules. It helps you visualize your data more effectively by highlighting specific values, ranges, or conditions, making it easier to interpret and analyze.
Getting Started with Conditional Formatting
To begin using conditional formatting in Google Sheets, follow these steps:
- Select the Data Range: First, select the cells or range of cells you want to format conditionally. This could be a single column, row, or a group of cells.
- Access Conditional Formatting: Navigate to the Format menu in the top toolbar and select Conditional formatting. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + F to access the conditional formatting dialog box directly.
- Define the Rule: In the conditional formatting dialog, you'll see a Format rules section. Click on Add new rule to create your first conditional formatting rule.
- Choose a Formatting Style: Google Sheets offers a range of formatting options, including font color, background color, borders, and custom formatting. You can apply these styles to your data based on the conditions you set.
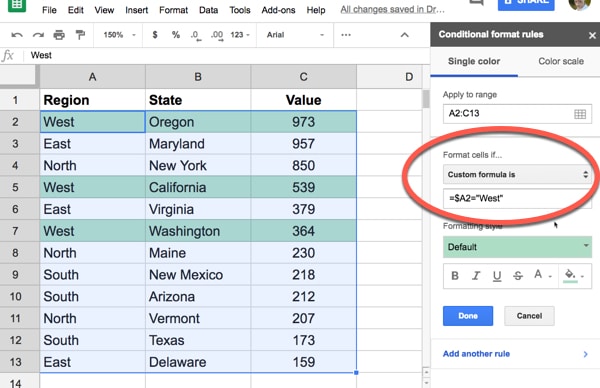
- Set the Condition: This is where you define the criteria for applying the formatting. You can choose from a variety of conditions, such as text containing specific words, values being greater than or less than a certain number, dates falling within a range, and more.
- Preview and Apply: Once you've set your condition and chosen the formatting style, you can preview how your data will look. If you're satisfied, click Done to apply the conditional formatting to your selected range.
Basic Conditional Formatting Examples
Let’s explore some simple yet practical examples of conditional formatting to understand its potential.
Highlighting Positive and Negative Values
Imagine you have a dataset with financial data, and you want to quickly identify positive and negative values. You can use conditional formatting to achieve this:
- Select the range of cells containing your financial data.
- Go to Format > Conditional formatting and create a new rule.
- Set the condition to Greater than and enter the value 0 in the corresponding field.
- Choose a formatting style, such as a green background color, to highlight positive values.
- Create another rule with the condition Less than and value 0, and select a red background color to highlight negative values.
With these rules applied, your positive values will be highlighted in green, and negative values in red, making it easy to spot the financial trends.
Identifying Top Performers
Suppose you have a sales report with a column showing the sales performance of different products. You want to quickly identify the top-performing products.
- Select the column containing the sales data.
- Apply conditional formatting with the condition Greater than and enter the value you consider to be the top performance threshold.
- Choose a formatting style, like a bold font or a specific color, to highlight these top performers.
Now, you can easily see which products are exceeding your performance expectations.
Advanced Conditional Formatting Techniques
While basic conditional formatting is powerful, Google Sheets also offers advanced techniques to cater to more complex data analysis needs.
Using Formulas in Conditional Formatting
Instead of using predefined conditions, you can create custom formulas to define your conditional formatting rules. This allows you to apply more specific and flexible conditions to your data.
For example, you can use the ISERROR function to identify cells containing errors or the COUNTIF function to count the occurrences of specific values within a range. These formulas can be used in conditional formatting rules to format cells based on these criteria.
Managing Multiple Rules and Priorities
When working with multiple conditional formatting rules, it’s important to manage their priorities. Google Sheets allows you to set the order in which rules are applied, ensuring that the most specific or important rules take precedence.
You can also create custom rules that apply formatting based on the combination of multiple conditions. For instance, you can format cells that contain a specific text and are also within a certain date range.
Applying Conditional Formatting to Specific Data Types
Google Sheets provides specialized conditional formatting options for different data types, such as dates, numbers, and text. These options offer tailored formatting rules specific to each data type.
For instance, you can format cells based on the day of the week (e.g., highlight weekends in red), or format numbers based on their decimal values (e.g., highlight values ending with .00 in green).
Best Practices and Tips
To make the most of conditional formatting in Google Sheets, consider the following best practices:
- Keep it Simple: Start with basic rules and gradually add complexity. Over-formatting can make your data harder to read.
- Use Contrasting Colors: Ensure that the colors you choose for conditional formatting provide sufficient contrast to be easily distinguishable.
- Test Your Rules: Always test your conditional formatting rules with sample data to ensure they work as expected.
- Document Your Rules: Keep a record of your rules, especially if you're working on complex datasets. This helps in maintaining and troubleshooting your formatting.
- Use Custom Number Formats: In addition to conditional formatting, you can use custom number formats to display data in a more readable format without altering the actual values.
Conditional Formatting for Data Visualization
Conditional formatting is an excellent tool for creating visually appealing and informative data visualizations. By applying different formatting styles to your data, you can create heatmaps, color-coded charts, and more.
For instance, you can use conditional formatting to create a heatmap that visualizes the performance of different regions or products. This can be especially useful for identifying high-performing areas or areas that need improvement.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While conditional formatting is a powerful tool, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few troubleshooting tips:
- Unexpected Formatting: If you notice unexpected formatting changes, review your conditional formatting rules and ensure they are correctly applied to the intended cells.
- Missing Rules: Sometimes, conditional formatting rules may not appear in the Conditional formatting dialog. Ensure that the selected range of cells is correct and that you haven't accidentally deleted any rules.
- Formula Errors: If you're using formulas in your conditional formatting rules, double-check the formulas for any errors or typos.
Conclusion
Conditional formatting is a versatile and powerful feature in Google Sheets that enhances your data analysis and visualization capabilities. By understanding the basics and exploring advanced techniques, you can create dynamic and informative datasets that highlight key insights. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced data analyst, conditional formatting is a valuable tool to have in your toolkit.
Can I apply multiple conditional formatting rules to a single cell or range of cells?
+Yes, you can apply multiple conditional formatting rules to a single cell or range of cells. Google Sheets allows you to stack multiple rules on top of each other, and they will be applied in the order you set.
How do I remove conditional formatting from a cell or range of cells?
+To remove conditional formatting, select the cell or range of cells and go to the Format menu. Choose Conditional formatting and then click on the Remove rules option. You can also use the keyboard shortcut Cmd/Ctrl + Shift + F to access the conditional formatting dialog, and then select the rule(s) you want to remove.
Can I copy conditional formatting rules to another cell or range of cells?
+Yes, you can copy conditional formatting rules using the standard copy-paste method. Select the cell or range of cells with the conditional formatting, copy them (Cmd/Ctrl + C), and then paste (Cmd/Ctrl + V) the formatting onto the new cell or range of cells.
How do I manage the priority of conditional formatting rules?
+To manage the priority of conditional formatting rules, select the cell or range of cells and go to the Format menu. Choose Conditional formatting and then click on the Edit rules option. In the dialog box, you can reorder the rules by dragging and dropping them to ensure the most specific or important rules take precedence.



