Mastering the FreeBSD Boot Menu: 5 Tips
The FreeBSD boot menu is a powerful tool that allows users to customize their boot process and troubleshoot various system issues. It provides an interface to select different boot options, load alternative kernels, and configure boot-time parameters. In this article, we will explore five essential tips to help you master the FreeBSD boot menu and unlock its full potential.
Understanding the Boot Menu Interface
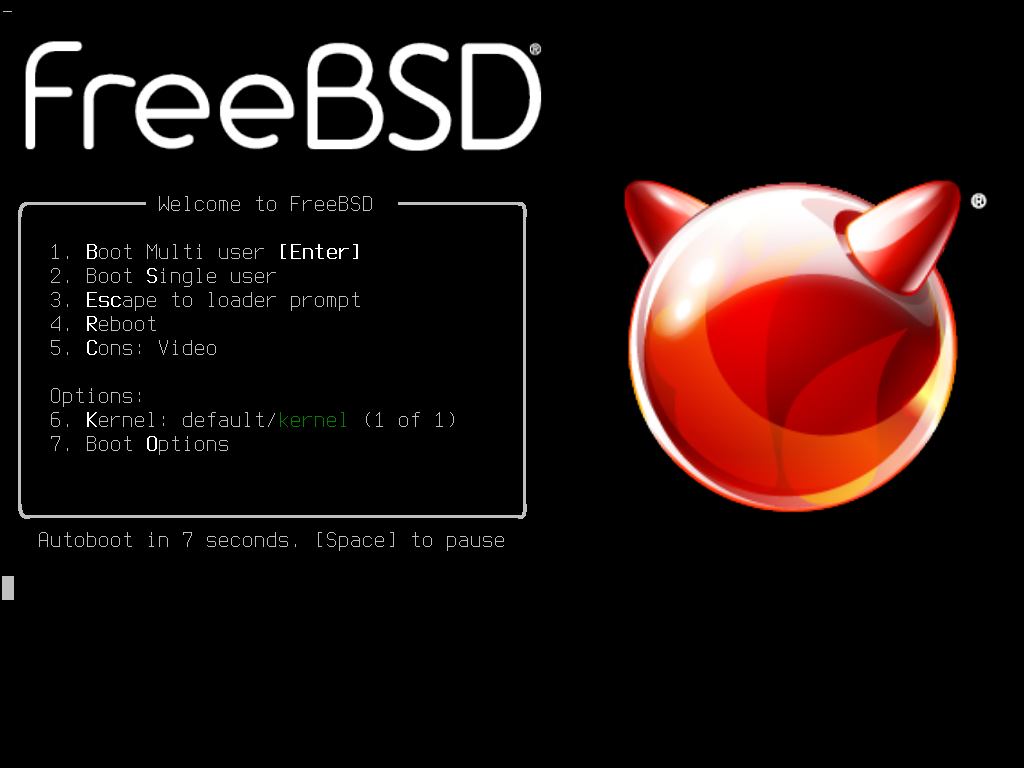
The FreeBSD boot menu offers a straightforward and intuitive interface. When the system boots, you will see a menu with various options. The default option is usually boot> , which initiates the normal boot process. However, the boot menu provides additional choices to customize the boot sequence.
Here's a breakdown of the key components of the FreeBSD boot menu:
- Boot Menu Options: These are the different boot choices available, each denoted by a number. The options may include booting from a specific kernel, booting into single-user mode, or loading a custom configuration.
- Default Timeout: The boot menu displays a countdown timer. If no option is selected before the timer expires, the default boot option will be executed.
- Cursor Navigation: Use the arrow keys to navigate through the available boot options. The currently selected option is highlighted.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: The boot menu supports keyboard shortcuts for quick actions. For instance, pressing Enter will boot the currently selected option, while pressing Esc may display advanced boot options.
Tip 1: Exploring Boot Menu Options
The FreeBSD boot menu provides a range of options to cater to different needs. By default, you will see the standard boot options, but you can access additional choices by pressing specific keys.
- Boot from Specific Kernel: You can select a particular kernel version to boot from. This is useful for testing new kernels or rolling back to a stable version.
- Single-User Mode: Entering single-user mode allows you to perform administrative tasks without starting the full operating system. It is ideal for troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Safe Mode: Similar to single-user mode, safe mode starts the system with minimal services and drivers. It is useful for diagnosing hardware issues or resolving boot-related problems.
- Custom Configuration: Some boot menu options allow you to load a custom configuration file. This is beneficial for testing experimental settings or applying temporary changes.
Tip 2: Customizing Boot Timeout
The default timeout for the FreeBSD boot menu is set to a specific duration. However, you can adjust this timeout to suit your preferences or system requirements.
To customize the boot timeout:
- Open the /boot/loader.conf file using a text editor.
- Locate the autoboot option. This option defines the timeout duration in seconds.
- Change the value of autoboot to your desired timeout. For example, autoboot=10 sets a 10-second timeout.
- Save the file and reboot your system to apply the changes.
Tip 3: Accessing Advanced Boot Options
The FreeBSD boot menu offers advanced options for experienced users and administrators. These options provide fine-grained control over the boot process and allow for advanced troubleshooting.
To access advanced boot options:
- Press Esc during the boot menu countdown.
- You will see a list of advanced options, including:
- kld_list: Load additional kernel modules.
- kernel_options: Set boot-time kernel parameters.
- loader_conf: Edit the /boot/loader.conf file directly.
- dump_conf: Configure dump device and options.
Tip 4: Booting from USB or Network
FreeBSD supports booting from various media, including USB drives and network interfaces. This flexibility allows you to create portable installations or boot from a network-based image.
To boot from USB or network:
- Connect your USB drive or configure your network boot settings.
- During the boot menu countdown, press F2 or F12 (depending on your system) to access the boot device selection menu.
- Select the desired boot device (e.g., USB Mass Storage Device or Network Boot).
- Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the boot process.
Tip 5: Troubleshooting with Boot Menu
The FreeBSD boot menu is a valuable tool for troubleshooting boot-related issues. It allows you to load different kernels, modify boot options, and access diagnostic tools.
Here are some troubleshooting tips using the boot menu:
- Single-User Mode: Boot into single-user mode to fix critical system issues or recover from a failed update.
- Safe Mode: Start the system in safe mode to identify and resolve hardware conflicts or driver problems.
- Kernel Debugging: Load a debug kernel to gather detailed information about system crashes or hangs.
- Custom Boot Options: Use custom boot options to disable specific services or drivers, helping to narrow down the cause of a boot failure.
Conclusion

Mastering the FreeBSD boot menu empowers you to customize your boot process, troubleshoot issues, and fine-tune your system's behavior. By understanding the boot menu interface, exploring its options, and customizing settings, you can unlock the full potential of FreeBSD and ensure a smooth and reliable boot experience.
How do I access the FreeBSD boot menu during bootup?
+
To access the FreeBSD boot menu, simply press the appropriate key during the boot process. The default key is usually Esc, but some systems may use F2 or F12. Pressing this key will pause the boot sequence and display the boot menu options.
Can I change the default boot option in the FreeBSD boot menu?
+
Yes, you can customize the default boot option in the FreeBSD boot menu. Open the /boot/loader.conf file and modify the default option. Set the desired boot option as the default by specifying its number or name. For example, default=“2” will set the second boot option as the default.
How do I boot into single-user mode using the FreeBSD boot menu?
+
To boot into single-user mode in FreeBSD, select the appropriate boot option from the boot menu. Look for an option labeled “Single-User Mode” or similar. Press Enter to boot into this mode, which provides a minimal environment for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Is it possible to customize boot-time kernel parameters using the FreeBSD boot menu?
+
Absolutely! The FreeBSD boot menu allows you to customize boot-time kernel parameters. During the boot process, press Esc to access advanced options. From there, select the kernel_options option. This will present a prompt where you can enter your desired kernel parameters. For example, you can set the debug parameter to enable kernel debugging.
What are some common keyboard shortcuts used in the FreeBSD boot menu?
+
The FreeBSD boot menu supports several keyboard shortcuts for convenience. Here are some common ones:
- Enter: Boots the currently selected option.
- Esc: Accesses advanced boot options.
- Arrow Keys: Navigates through boot menu options.
- F2/F12: Opens the boot device selection menu.