Format True or False: Excel's Easy Guide
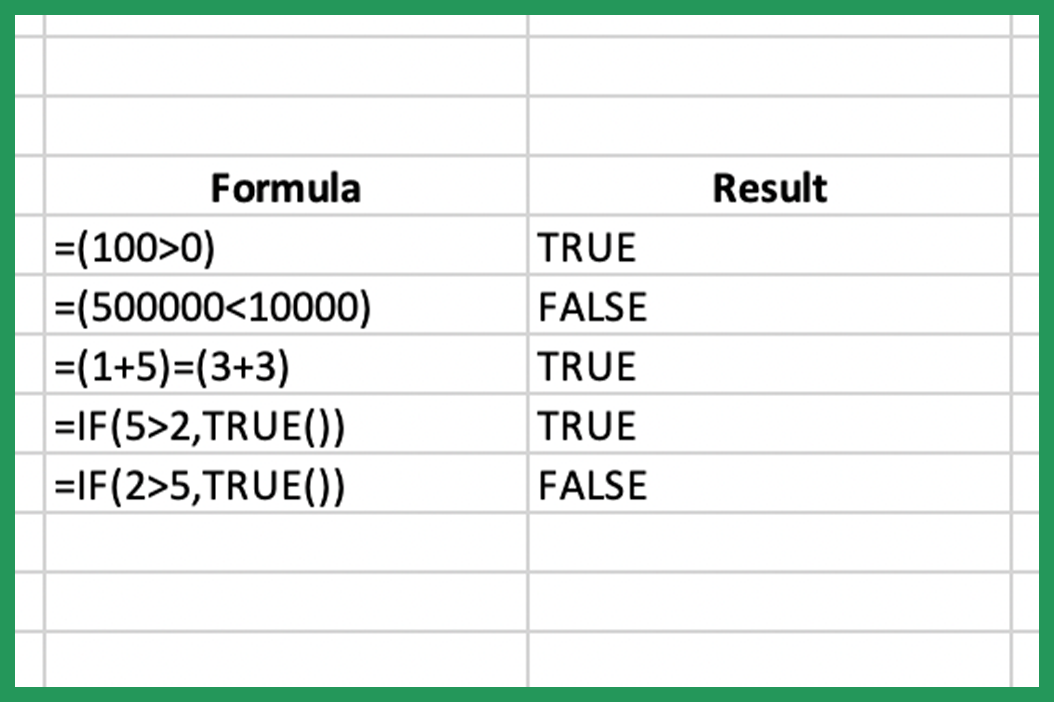
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Microsoft Excel, the powerful spreadsheet software that has become an indispensable tool for professionals and individuals alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of Excel, exploring its capabilities, features, and best practices. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will provide you with valuable insights and tips to enhance your Excel skills and productivity.
Unveiling the Power of Excel: True or False Statements
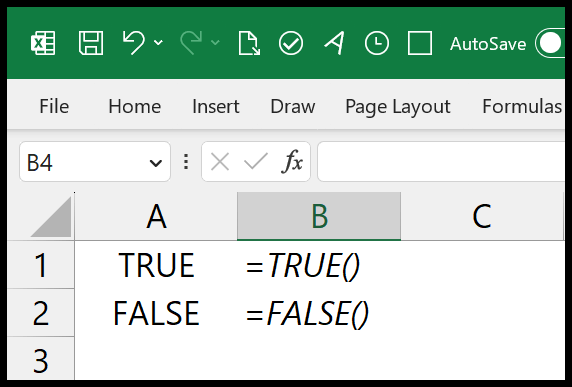
Excel is more than just a simple spreadsheet program; it is a versatile tool that offers an extensive range of functions and capabilities. To better understand its potential, let’s uncover some true or false statements about Excel and explore the truth behind its power.
Excel’s Functionality is Limited to Basic Calculations
False. While Excel is renowned for its calculation capabilities, it goes far beyond simple arithmetic. Excel provides a vast library of functions and formulas that cater to various data analysis needs. From financial calculations to statistical analysis, data manipulation, and even complex modeling, Excel offers an extensive toolkit for professionals in different industries.
| Function Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Financial Functions | PV, FV, NPV, IRR, PMT |
| Statistical Functions | AVERAGE, MEDIAN, COUNTIF, SUMIF |
| Date & Time Functions | TODAY, YEARFRAC, WORKDAY |
| Text Functions | CONCAT, LEFT, UPPER |
| Lookup Functions | VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, XLOOKUP |
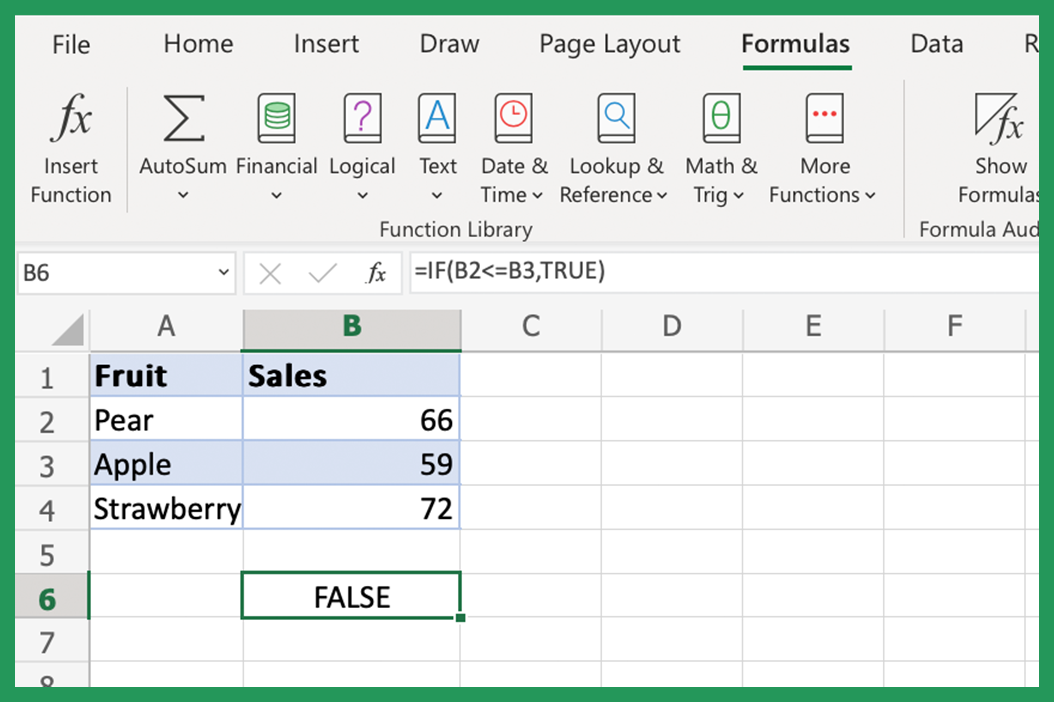
These functions, along with many others, empower users to perform advanced data analysis, automate repetitive tasks, and make informed decisions based on accurate calculations.
Excel is Only Suitable for Financial Professionals
False. Excel’s versatility extends far beyond the realm of finance. While it is undoubtedly a powerful tool for financial analysts and accountants, Excel finds applications in various fields, including data science, research, project management, and even creative industries.
- Data Science: Excel provides a robust platform for data manipulation, cleaning, and analysis. Its ability to handle large datasets, perform statistical calculations, and create visualizations makes it an essential tool for data scientists and analysts.
- Research: Researchers across disciplines rely on Excel for organizing and analyzing research data. Its flexibility allows for efficient data management, from tracking survey responses to conducting complex analyses.
- Project Management: Excel simplifies project planning and tracking. Users can create detailed project timelines, assign tasks, monitor progress, and manage resources, all within the familiar Excel interface.
- Creative Industries: Even in creative fields like design and marketing, Excel plays a vital role. Designers use Excel for organizing color palettes, tracking design assets, and managing project budgets. Marketers leverage Excel for data-driven campaigns, analyzing customer behavior, and optimizing strategies.
Excel is Difficult to Learn and Master
True… and False. While Excel has a steep learning curve, its vast capabilities and user-friendly interface make it accessible to beginners and experts alike. The key to mastering Excel lies in understanding its core principles and gradually exploring its advanced features.
Beginners can start with basic functions, formatting, and data entry to grasp the fundamentals. As they gain confidence, they can explore more advanced features like macros, pivot tables, and data visualization tools. Excel's extensive documentation, online tutorials, and community support make it easier to learn and overcome challenges.
Excel’s Practical Applications: Real-World Examples
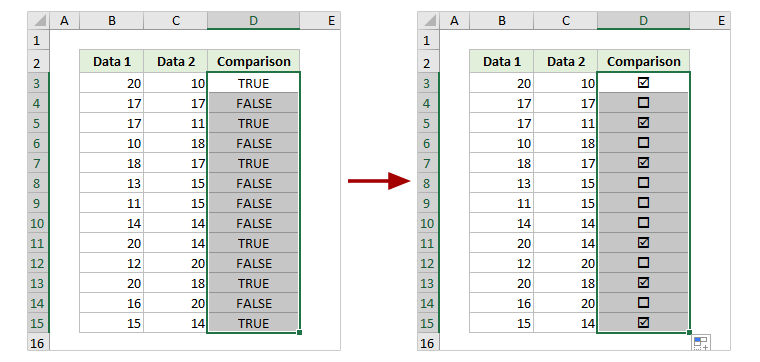
To further illustrate Excel’s versatility, let’s explore some real-world examples of how professionals across industries leverage its power.
Financial Analysis and Budgeting
Financial analysts and accountants rely on Excel for various tasks, including financial modeling, budget planning, and forecasting. With Excel’s advanced functions and formulas, professionals can create dynamic models that simulate different scenarios, perform what-if analyses, and make informed financial decisions.
Data Analysis and Visualization
Excel is a go-to tool for data analysts and researchers. Its powerful data manipulation capabilities, coupled with its extensive visualization options, enable users to clean, transform, and analyze data. Excel’s charts, graphs, and pivot tables help visualize data trends, patterns, and insights, making complex data more accessible and understandable.
Project Management and Tracking
Project managers use Excel to plan, track, and manage projects efficiently. They create detailed project timelines, assign tasks to team members, and monitor progress using Excel’s features like conditional formatting and custom formulas. Excel’s flexibility allows project managers to adapt their tracking systems to their specific project needs.
Inventory Management and Sales Tracking
Businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, often use Excel for inventory management and sales tracking. With Excel, they can create dynamic spreadsheets to monitor stock levels, track sales performance, and analyze customer trends. This enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding inventory procurement, sales strategies, and customer engagement.
Tips and Tricks for Excel Efficiency
To maximize your Excel productivity and efficiency, here are some valuable tips and tricks:
Utilize Keyboard Shortcuts
Mastering Excel’s keyboard shortcuts can significantly speed up your workflow. Familiarize yourself with commonly used shortcuts like Ctrl + C (copy), Ctrl + V (paste), Ctrl + Z (undo), and Ctrl + Home (go to the beginning of the worksheet). These shortcuts save time and improve your overall efficiency.
Learn Advanced Functions and Formulas
Excel’s advanced functions and formulas are powerful tools for data analysis and manipulation. Invest time in learning functions like VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, SUMIFS, and IFERROR. These functions enable you to perform complex calculations, extract specific data, and automate repetitive tasks, enhancing your productivity and accuracy.
Create Custom Templates
Excel allows you to create custom templates for repetitive tasks or projects. By designing and saving templates with predefined formulas, formatting, and data structures, you can streamline your workflow and ensure consistency across different projects. Templates save time and reduce the risk of errors.
Master Pivot Tables and Charts
Pivot tables and charts are powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing data. Learn how to create and manipulate pivot tables to summarize large datasets and gain valuable insights. Additionally, explore Excel’s charting options to create visually appealing and informative charts that communicate your data effectively.
Utilize Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting is a powerful feature that allows you to highlight and visualize data based on specific conditions. You can use conditional formatting to quickly identify trends, anomalies, or important data points. It enhances data analysis and makes your spreadsheets more visually engaging.
Excel’s Future and Continuous Evolution
Excel has come a long way since its inception, and its development continues to evolve with the changing needs of users. Microsoft, the creator of Excel, actively listens to user feedback and regularly introduces new features and improvements.
One of the significant advancements in recent years is the introduction of Excel Online, a web-based version of Excel that allows users to access and edit spreadsheets directly from their browsers. This cloud-based solution enhances collaboration and accessibility, enabling teams to work together seamlessly on projects, regardless of their physical location.
Furthermore, Excel's integration with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and PowerPoint, has been enhanced, making it easier to incorporate Excel data and visualizations into other documents. This integration streamlines workflows and enables users to present their data effectively across different platforms.
As technology advances, Excel continues to embrace new features and capabilities. For instance, Excel now supports Power Query, a powerful data transformation and loading tool, enabling users to extract, transform, and load data from various sources with ease. Additionally, Excel's integration with Power BI, Microsoft's business analytics service, allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports, empowering data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion
Excel, with its vast functionality and versatility, has become an indispensable tool for professionals and individuals across various industries. From basic calculations to advanced data analysis, Excel empowers users to unlock the potential of their data and make informed decisions. By understanding its capabilities, exploring real-world applications, and adopting efficient practices, you can maximize your Excel skills and productivity.
Whether you are a finance professional, data analyst, project manager, or creative professional, Excel offers a comprehensive toolkit to streamline your work and enhance your productivity. Embrace the power of Excel, and unlock a world of efficiency and data-driven success.
FAQ
Can Excel handle large datasets efficiently?
+Yes, Excel is designed to handle large datasets efficiently. With its advanced filtering, sorting, and data manipulation capabilities, you can work with extensive datasets without compromising performance. Excel’s data management tools and formulas allow you to analyze and derive insights from large amounts of information.
How can I learn Excel effectively?
+Learning Excel effectively involves a combination of online tutorials, practice, and hands-on experience. Start with basic tutorials to grasp the fundamentals, then gradually explore advanced features. Practice with real-world datasets and challenge yourself to apply what you’ve learned. Online communities and forums can also provide valuable insights and support.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in Excel?
+Common Excel mistakes include forgetting to save your work regularly, using incorrect formulas or functions, and neglecting data validation. It’s crucial to save your work frequently to avoid data loss. Always double-check formulas and functions for accuracy, and utilize data validation to ensure data integrity. Additionally, avoid hardcoding values and instead use cell references for flexibility.
How can I improve my Excel visualization skills?
+Improving your Excel visualization skills involves understanding your data and choosing the appropriate chart type to represent it effectively. Explore different chart types, such as bar charts, line charts, pie charts, and scatter plots, to find the best fit for your data. Practice creating visually appealing and informative charts that convey your data’s key insights.
Is Excel suitable for data science and machine learning tasks?
+Excel can be a useful tool for data science and machine learning tasks, especially for data cleaning, transformation, and initial data exploration. However, for more complex machine learning algorithms and large-scale data processing, specialized tools like Python or R may be more suitable. Excel’s limitations in handling extremely large datasets and its lack of advanced statistical and machine learning libraries make it less ideal for advanced data science tasks.