Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius: 5 Easy Tips
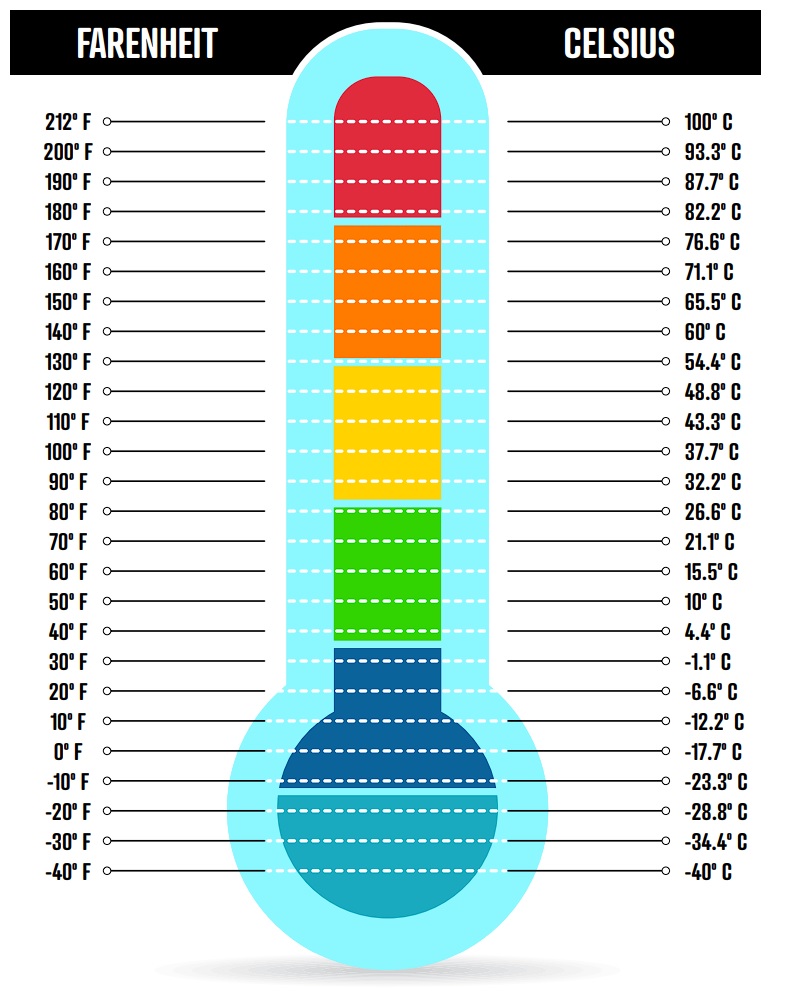
Converting temperatures from Fahrenheit to Celsius is a common task, especially when traveling internationally or working with diverse datasets. This guide will provide you with five easy tips to master this essential skill, ensuring you can accurately convert temperatures with ease.
Understanding the Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales

Before we delve into the conversion tips, let’s quickly review the basic principles of the Fahrenheit and Celsius temperature scales.
The Fahrenheit scale, named after its inventor Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. It is based on three reference points: the freezing point of water is set at 32 °F, and the boiling point of water is set at 212 °F. The scale is divided into 180 equal parts, with each degree representing a fixed change in temperature.
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is the most widely used temperature scale worldwide. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, who initially proposed a reverse version of the scale. In the Celsius scale, the freezing point of water is set at 0 °C, and the boiling point is set at 100 °C. The scale is divided into 100 equal parts, making it a simpler and more intuitive system for everyday use.
Tip 1: The Basic Conversion Formula

The most fundamental method to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is by using the following formula:
°C = (°F - 32) x 5/9
This formula provides an accurate conversion for any given temperature in Fahrenheit. Let's apply this formula to a simple example:
If you want to convert 70 °F to Celsius, you would calculate:
°C = (70 - 32) x 5/9
Solving the equation, you get:
°C = 21.11 °C
So, 70 °F is approximately equal to 21.11 °C.
Tip 2: Using Online Converters
In today’s digital age, you don’t have to rely solely on manual calculations. Numerous online temperature converters are available that can instantly perform the conversion for you. These converters are user-friendly and often provide additional features, such as reverse conversions (Celsius to Fahrenheit) and the ability to convert multiple temperatures at once.
Here's a step-by-step guide to using an online converter:
- Open your preferred web browser and search for a reputable temperature converter.
- Enter the temperature you want to convert in Fahrenheit.
- Select the units you want to convert to (in this case, Celsius).
- Click on the "Convert" or "Calculate" button.
- The converter will instantly display the converted temperature.
Some popular online converters include ConvertUnits.com, TemperatureConverter.org, and UnitJuggler.com. These websites are reliable and easy to use, ensuring accurate conversions with just a few clicks.
Tip 3: Memorizing Key Conversion Points
While having a basic understanding of the conversion formula is essential, memorizing a few key conversion points can be a valuable shortcut. Here are some temperature points that are worth remembering:
| Fahrenheit | Celsius |
|---|---|
| 32 °F | 0 °C |
| 50 °F | 10 °C |
| 70 °F | 21 °C |
| 86 °F | 30 °C |
| 100 °F | 38 °C |

By memorizing these conversions, you can quickly estimate the approximate Celsius equivalent of common Fahrenheit temperatures. This is especially useful when you need a rough idea of the temperature without the need for precise calculations.
Tip 4: Using Conversion Apps

For those who frequently need to convert temperatures, using a dedicated conversion app can be incredibly convenient. These apps are available for both smartphones and desktop computers, providing quick and accurate conversions at your fingertips.
Some popular conversion apps include:
- Converter Plus (for iOS and Android): This app offers a simple and intuitive interface, allowing you to convert temperatures, currencies, and various other units with ease.
- Convert Pad (for Windows and macOS): Convert Pad is a lightweight and user-friendly app that supports a wide range of unit conversions, including temperature conversions.
- Unit Converter Ultimate (for Android): This app provides an extensive list of conversion categories, including temperature, length, weight, and more. It also offers a history feature to track your previous conversions.
These apps are designed to simplify the conversion process, making it quick and effortless to switch between Fahrenheit and Celsius.
Tip 5: Practice with Real-World Examples
The best way to master temperature conversions is through practice. Seek out real-world scenarios where you can apply your conversion skills. Here are a few examples to get you started:
- Convert the temperature of a hot summer day in the US (e.g., 95 °F) to Celsius.
- Determine the Celsius equivalent of a typical winter day in a European city (e.g., 30 °F in New York City, USA).
- Calculate the temperature in Celsius when a recipe calls for baking at 350 °F.
By practicing with these examples and others, you'll gain confidence in your conversion abilities and be better equipped to handle temperature conversions in various contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do some countries use Fahrenheit, while others use Celsius?
+The choice of temperature scale is often a matter of historical and cultural preference. Fahrenheit, being the older scale, was widely adopted in the US and a few other countries. On the other hand, Celsius gained popularity due to its simplicity and ease of use, making it the preferred scale for scientific and international contexts.
Are there any temperature scales other than Fahrenheit and Celsius?
+Yes, there are other temperature scales, but they are less commonly used in everyday contexts. For example, the Kelvin scale is used in scientific and engineering applications, with absolute zero as its starting point. Additionally, the Rankine scale is sometimes used in certain engineering fields.
How accurate are online temperature converters and apps?
+Online converters and apps are generally very accurate, as they rely on standardized conversion formulas. However, it’s always a good practice to double-check your results, especially when dealing with critical applications or scientific research.


