The 6 Sigma Checklist: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of quality management, Six Sigma stands as a powerful methodology that has revolutionized processes across industries. Its impact is evident in the consistent delivery of exceptional results, making it a sought-after approach for organizations aiming for operational excellence.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the Six Sigma Checklist, a vital tool that underpins the success of any Six Sigma initiative. By understanding and implementing this checklist, professionals can navigate the Six Sigma process with precision and ensure sustainable quality improvements.
Understanding the Six Sigma Checklist

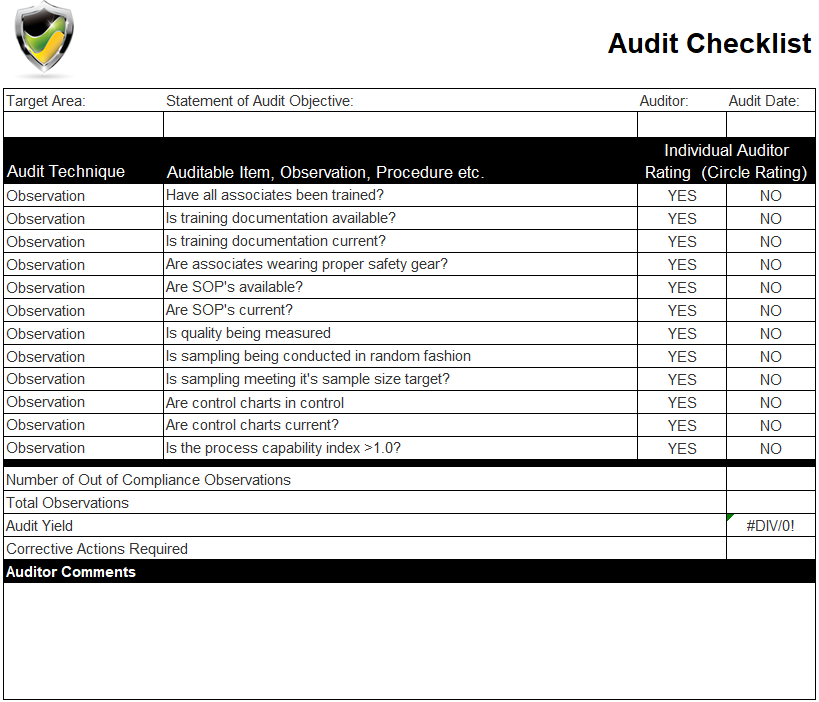
The Six Sigma Checklist serves as a structured roadmap, guiding practitioners through the various stages of a Six Sigma project. It encompasses a range of critical elements, each playing a pivotal role in achieving the project’s objectives.
At its core, the checklist is designed to ensure that all necessary steps are taken, from project initiation to closure, leaving no room for oversight or error. By following this comprehensive guide, organizations can streamline their processes, identify and mitigate risks, and ultimately, achieve their quality goals.
Key Elements of the Six Sigma Checklist
- Define Phase: This initial stage sets the foundation for the entire project. It involves defining the problem or opportunity, establishing clear goals and objectives, and identifying the project’s scope and boundaries.
- Measure Phase: Here, the focus shifts to data collection and analysis. Practitioners gather relevant data, assess process performance, and establish baseline metrics. This phase is crucial for understanding the current state of the process and identifying areas for improvement.
- Analyze Phase: With data in hand, the analyze phase delves into root cause analysis. Practitioners employ various tools and techniques to identify the underlying causes of process issues. This phase is critical for developing effective solutions and strategies.
- Improve Phase: In this phase, the focus is on implementing solutions. Practitioners test and validate potential improvements, ensuring they are effective and sustainable. This phase often involves collaboration across teams and stakeholders to ensure successful implementation.
- Control Phase: The control phase ensures that the improvements made are maintained over time. It involves establishing control mechanisms, monitoring process performance, and taking corrective actions as needed. This phase is essential for sustaining the gains achieved through the Six Sigma project.
The Benefits of a Comprehensive Checklist

Implementing a comprehensive Six Sigma Checklist offers a multitude of benefits to organizations and their quality initiatives.
First and foremost, it ensures a structured and disciplined approach to quality improvement. By following a predefined checklist, practitioners can avoid common pitfalls and ensure that all critical aspects of the project are addressed. This structured approach leads to more efficient and effective project execution.
Secondly, the checklist serves as a valuable tool for knowledge transfer and consistency. It provides a standardized framework that can be adopted across different projects and teams. This consistency ensures that best practices are shared and applied consistently, leading to more predictable and reliable outcomes.
Additionally, the checklist acts as a risk mitigation tool. By identifying potential risks and challenges early on, practitioners can develop strategies to address them proactively. This risk-based approach minimizes the impact of unforeseen issues and helps maintain project momentum.
Real-World Application and Success Stories
The impact of the Six Sigma Checklist is evident in numerous success stories across diverse industries.
For instance, in the manufacturing sector, a leading automotive company utilized the checklist to address a persistent issue with product defects. By following the structured steps, they were able to identify the root causes of the defects and implement effective solutions. The result was a significant reduction in defect rates, leading to improved customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
In the healthcare industry, a prominent hospital adopted the Six Sigma Checklist to enhance its patient experience. By defining clear goals and measuring key performance indicators, they identified areas where process improvements could enhance patient satisfaction. Through the analyze and improve phases, they implemented changes that streamlined patient flow, reduced wait times, and improved overall patient care.
| Industry | Impact of Six Sigma Checklist |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Reduced product defects, improved customer satisfaction, increased profitability |
| Healthcare | Enhanced patient experience, streamlined processes, improved patient care |
| Service Sector | Improved customer service, increased operational efficiency, reduced costs |

Best Practices for Utilizing the Checklist
To maximize the benefits of the Six Sigma Checklist, practitioners should consider the following best practices:
- Clear Definition of Goals: Ensure that project goals and objectives are well-defined and aligned with organizational priorities. This clarity sets the direction for the entire project.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Rely on data and metrics to drive decision-making throughout the project. This approach ensures that improvements are based on factual evidence rather than assumptions.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between different teams and departments. By involving stakeholders from various areas, organizations can leverage diverse expertise and ensure a holistic approach to quality improvement.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment: The Six Sigma Checklist is a living document. Practitioners should regularly review and update the checklist based on project progress and evolving requirements. This flexibility ensures that the checklist remains relevant and effective.
Conclusion
The Six Sigma Checklist is an indispensable tool for organizations committed to achieving operational excellence. By embracing this comprehensive guide, professionals can navigate the Six Sigma process with confidence and precision. The structured approach ensures that quality initiatives are well-planned, executed efficiently, and deliver sustainable results.
As organizations continue to prioritize quality and process improvement, the Six Sigma Checklist will remain a cornerstone of their success, guiding them towards excellence in all their endeavors.
What is the significance of the Define Phase in the Six Sigma Checklist?
+The Define Phase is crucial as it sets the foundation for the entire Six Sigma project. It involves defining the problem or opportunity, establishing clear goals, and identifying the project’s scope. A well-defined project ensures that all subsequent phases are aligned with the desired outcomes.
How does the Measure Phase contribute to the overall success of a Six Sigma project?
+The Measure Phase is essential as it provides the data and insights needed to understand the current state of the process. By gathering relevant data and establishing baseline metrics, practitioners can identify areas for improvement and set realistic targets for the project.
What are some common challenges faced during the Analyze Phase, and how can they be addressed?
+The Analyze Phase can be challenging due to the complexity of identifying root causes. To address this, practitioners should employ a range of tools and techniques, such as cause-and-effect diagrams and statistical analysis. Additionally, involving subject matter experts can provide valuable insights and guide the analysis process.